An IP Subnet Calculator is an essential tool for network administrators, IT professionals, and networking students. It simplifies the complex process of dividing IP networks into smaller, manageable subnets. Whether you’re designing a new network infrastructure, troubleshooting connectivity issues, or studying for networking certifications, understanding how subnet calculations work is crucial for effective network management.
What is Subnetting?
Subnetting is the practice of dividing a large IP network into smaller, more manageable sub-networks or subnets. This division creates logical boundaries within a network, allowing for more efficient routing, improved security, and better IP address management.
Benefits of Subnetting
Improved Network Performance
By breaking a network into smaller segments, subnetting reduces network congestion and broadcast traffic. Each subnet operates as its own broadcast domain, limiting the reach of broadcast messages and improving overall network efficiency.
Enhanced Security
Subnets create natural security boundaries. Network administrators can implement access control lists (ACLs) and firewall rules between subnets to control traffic flow and protect sensitive resources from unauthorized access.
Efficient IP Address Utilization
Subnetting allows organizations to allocate IP addresses more efficiently by creating subnets that match the actual number of hosts needed in each network segment, reducing IP address waste.
Simplified Network Management
With proper subnetting, network troubleshooting becomes easier as problems can be isolated to specific subnets. It also facilitates organized network growth and expansion.
Key Subnetting Terminology
Before diving into subnet calculations, it’s essential to understand the fundamental terminology used in IP networking and subnetting:
IP Address
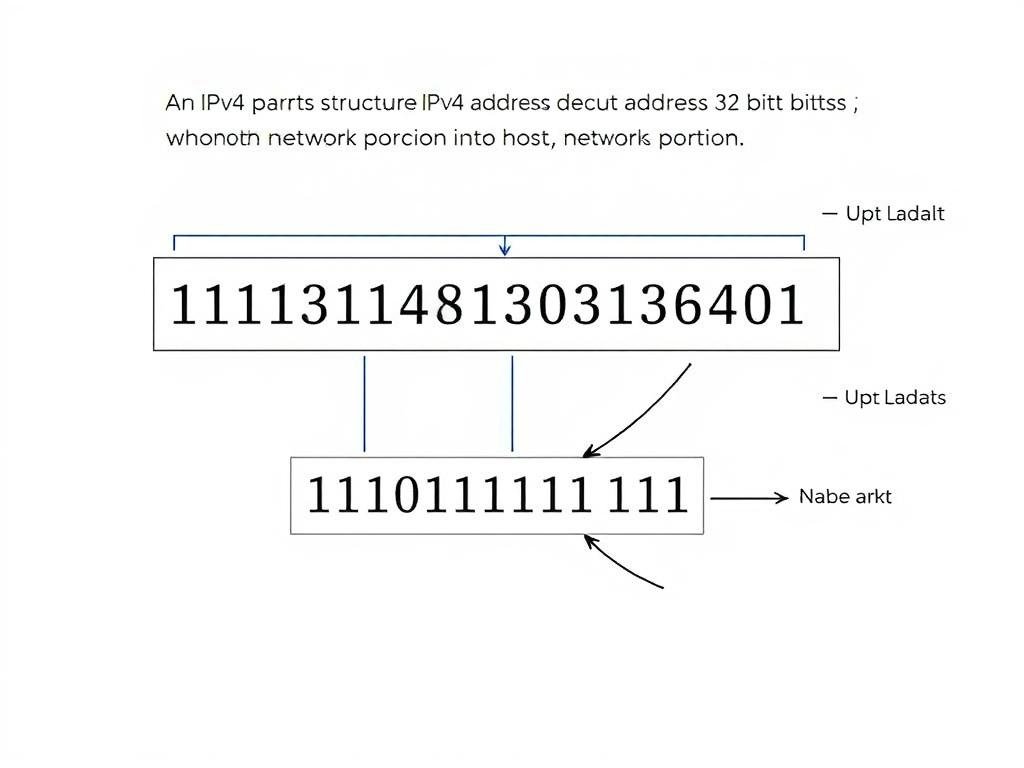
An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. In IPv4, it consists of 32 bits typically represented as four octets in decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Each IP address has two components: a network portion and a host portion.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a 32-bit value that determines which portion of an IP address refers to the network address and which portion refers to the host address. It’s represented in the same format as an IP address (e.g., 255.255.255.0) or using CIDR notation.
CIDR Notation
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation is a compact method for specifying IP addresses and their associated routing prefix. It’s written as the IP address followed by a forward slash and the number of bits in the network mask (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24).
| CIDR Notation | Subnet Mask | Number of Usable Hosts |
| /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 254 |
| /25 | 255.255.255.128 | 126 |
| /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 62 |
| /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 30 |
| /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 14 |
Network Address
The network address is the first address in a subnet and identifies the subnet itself. It’s calculated by performing a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask. Network addresses cannot be assigned to devices.
Broadcast Address
The broadcast address is the last address in a subnet and is used to send data to all devices within that subnet. It’s calculated by setting all host bits to 1 in the network address. Like the network address, the broadcast address cannot be assigned to devices.
Usable Host Range
The usable host range consists of all IP addresses between the network address and the broadcast address. These are the addresses that can be assigned to devices on the subnet.

IP Address Classes and Subnet Masks
Traditionally, IPv4 addresses were divided into five classes (A through E), each with a default subnet mask. Although modern networking uses classless addressing (CIDR), understanding the class system helps grasp the fundamentals of IP addressing.
Class A
Range: 1.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255
Default subnet mask: 255.0.0.0 (/8)
First bit: 0
Available hosts: 16,777,214
Class B
Range: 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
Default subnet mask: 255.255.0.0 (/16)
First bits: 10
Available hosts: 65,534
Class C
Range: 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
Default subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 (/24)
First bits: 110
Available hosts: 254
Classes D (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255) and E (240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255) are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes, respectively, and are not used for regular host addressing.
How Subnet Calculation Works
Subnet calculation involves determining various network parameters based on an IP address and subnet mask. Understanding the process helps network administrators design and troubleshoot networks effectively.
Step-by-Step Subnet Calculation Process
- Identify the IP address and subnet mask – Start with the given IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.10) and subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0 or /24).
- Convert to binary – Convert both the IP address and subnet mask to binary format to perform the necessary calculations.
- Calculate the network address – Perform a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and subnet mask to determine the network address.
- Calculate the broadcast address – Invert the subnet mask (creating a wildcard mask), perform a bitwise OR operation with the network address to find the broadcast address.
- Determine the usable IP range – The first usable IP is one address above the network address, and the last usable IP is one address below the broadcast address.
- Calculate the total number of hosts – Use the formula 2^(32-prefix length) – 2 to determine the number of usable host addresses.
Skip the Complex Math
Subnet calculations involve binary math and can be error-prone when done manually. Our IP Subnet Calculator handles all these calculations instantly, saving you time and preventing mistakes.
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the subnet parameters for IP address 192.168.10.15 with subnet mask 255.255.255.240 (/28):
| Parameter | Value | Calculation |
| IP Address | 192.168.10.15 | Given |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.240 | Given (/28) |
| Network Address | 192.168.10.0 | IP AND Subnet Mask |
| Broadcast Address | 192.168.10.15 | Network OR (NOT Subnet Mask) |
| First Usable IP | 192.168.10.1 | Network Address + 1 |
| Last Usable IP | 192.168.10.14 | Broadcast Address – 1 |
| Number of Usable Hosts | 14 | 2^(32-28) – 2 |
Why Use an IP Subnet Calculator?
While understanding the manual calculation process is valuable for networking professionals, using an IP Subnet Calculator offers numerous advantages:
Advantages of Using an IP Subnet Calculator
- Speed and Efficiency – Calculate subnet parameters instantly, saving valuable time during network design and troubleshooting.
- Accuracy – Eliminate human error in binary conversions and mathematical operations.
- Comprehensive Results – Obtain all relevant subnet information in one place, including network address, broadcast address, usable IP range, and more.
- Educational Value – Learn subnetting concepts by observing the relationships between different parameters.
- Support for Various Subnet Sizes – Easily work with any subnet mask from /0 to /32.
- Visualization – Many calculators provide visual representations of subnets, making concepts easier to understand.
Challenges of Manual Calculation
- Time-Consuming – Manual calculations require multiple steps and conversions.
- Error-Prone – Binary conversions and bitwise operations are susceptible to mistakes.
- Complex for Large Networks – Calculating parameters for multiple subnets becomes increasingly difficult.
- Requires Deep Understanding – Manual calculation demands thorough knowledge of binary math and networking principles.
- Difficult to Verify – Without tools, verifying calculation accuracy is challenging.
- Limited Scope – Manual calculations typically focus on basic parameters, potentially missing valuable information.
Ready to Simplify Your Network Planning?
Our IP Subnet Calculator provides instant, accurate results for all your subnetting needs. Whether you’re designing a new network, studying for certifications, or troubleshooting connectivity issues, our tool makes subnet calculations effortless.
Practical Applications of IP Subnet Calculators
IP Subnet Calculators are versatile tools with applications across various networking scenarios:

Network Design
When planning a new network infrastructure, subnet calculators help determine the optimal subnet size based on the number of required hosts. They assist in creating efficient IP addressing schemes that accommodate future growth while minimizing wasted addresses.
Network Segmentation
For security and performance reasons, organizations often segment their networks into separate subnets. IP Subnet Calculators help determine the appropriate subnet masks and address ranges for each segment, ensuring proper isolation and communication.
Troubleshooting
When diagnosing connectivity issues, subnet calculators help verify whether devices are on the same subnet and can communicate directly. They also assist in identifying misconfigured subnet masks that may prevent proper communication.
VLSM Implementation
Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) allows for more efficient use of IP address space by using different subnet sizes within the same network. Subnet calculators are essential for planning and implementing VLSM designs.
Certification Preparation
Networking certifications like CompTIA Network+, CCNA, and others require proficiency in subnetting. IP Subnet Calculators serve as valuable learning tools for practicing and verifying subnet calculations.
IP Address Management
For organizations managing large IP address spaces, subnet calculators help track and allocate address blocks efficiently, preventing address conflicts and ensuring proper utilization of available addresses.
Mastering IP Subnetting with the Right Tools
Understanding IP subnetting is a fundamental skill for anyone working with computer networks. While the concepts may seem complex initially, they become more manageable with practice and the right tools. An IP Subnet Calculator simplifies the process by automating the mathematical calculations, allowing you to focus on the network design and implementation rather than the underlying binary operations.
Whether you’re a seasoned network administrator, an IT professional, or a student preparing for networking certifications, an IP Subnet Calculator is an invaluable tool in your networking toolkit. It not only saves time and reduces errors but also helps reinforce your understanding of subnetting principles through practical application.

Take the Complexity Out of Subnetting
Now that you understand the fundamentals of IP subnetting, put your knowledge into practice with our powerful and accurate IP Subnet Calculator. Get instant results for all your subnet calculations and focus on building better networks.