Use our Auto Lease Calculator to estimate monthly lease payments, total cost, and interest. Plan your vehicle lease and manage your budget effectively.
Leasing a car involves complex calculations that determine your monthly payments. An Auto Lease Calculator helps simplify this process, allowing you to make informed decisions before signing a lease agreement. This guide explains how these calculators work, breaks down key leasing terms, and provides a practical tool to estimate your payments accurately.
What is an Auto Lease Calculator?
An Auto Lease Calculator is a financial tool that helps estimate monthly lease payments based on several key variables. Unlike purchasing a car, where you pay for the entire vehicle, leasing involves paying only for the vehicle’s depreciation during your lease term, plus interest and fees.
These calculators take into account factors like the vehicle’s price, down payment, residual value, money factor (interest rate), and lease term to provide an accurate estimate of your monthly payments. Using an Auto Lease Calculator before visiting a dealership gives you valuable information to negotiate better terms.
Ready to Calculate Your Lease Payment?
Use our calculator below to get a quick estimate of your monthly payments.
Key Auto Leasing Terms Explained
Understanding the terminology used in auto leasing is essential for making informed decisions. Here are the key terms you’ll encounter when using an Auto Lease Calculator:
Capitalized Cost (Cap Cost)
The capitalized cost is the negotiated price of the vehicle you’re leasing. This is similar to the purchase price when buying a car, but it’s specifically what you and the dealer agree the car is worth for leasing purposes. Lowering this amount through negotiation or trade-ins directly reduces your monthly payments.
Residual Value
Residual value represents what the car is expected to be worth at the end of your lease term. This value is set by the leasing company based on industry projections. A higher residual value means lower monthly payments since you’re paying for less depreciation. Vehicles that hold their value well typically offer more attractive lease terms.
Leasing a car with a high residual value can save you thousands over the lease term. For example, a $30,000 car with a 60% residual after 36 months means you’re only financing $12,000 in depreciation.
Money Factor
The money factor is essentially the interest rate on your lease, but it’s expressed differently. To convert a money factor to an APR (Annual Percentage Rate), multiply it by 2,400. For example, a money factor of 0.00125 equals a 3% APR (0.00125 × 2,400 = 3%). A lower money factor means lower monthly payments.
Lease Term
The lease term is the length of your lease agreement, typically ranging from 24 to 48 months. Most leases run for 36 months, which often aligns with the vehicle’s warranty period. Longer terms can lower your monthly payment but may extend beyond the warranty coverage.
Mileage Allowance
Lease agreements include a mileage limit, commonly 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. Exceeding this limit results in excess mileage charges at the end of the lease, typically ranging from $0.10 to $0.25 per mile over the limit. Be realistic about your driving habits when selecting a mileage allowance.
How to Use an Auto Lease Calculator
Using an Auto Lease Calculator effectively requires understanding what information to input and how to interpret the results. Follow these steps to get accurate estimates:

- Gather necessary information: Vehicle price (MSRP or negotiated price), down payment amount, lease term, and estimated residual value.
- Enter the vehicle price: Input the negotiated price of the vehicle, not the MSRP (unless you’re paying full price).
- Add your down payment: Include any cash down payment, trade-in value, or rebates that reduce the capitalized cost.
- Input the residual value: If you know it, enter the residual value as a percentage or dollar amount. If not, most calculators estimate 50-60% for a 36-month lease.
- Enter the money factor: Input the interest rate or money factor. If you don’t know it, use your credit score as a guide (excellent: 2-3%, good: 4-5%, average: 6-7%).
- Specify the lease term: Select your desired lease length, typically 24, 36, or 48 months.
- Add sales tax rate: Enter your local sales tax rate, as this affects your monthly payment.
- Review the results: Analyze the calculated monthly payment and total lease cost.
Pro Tip: Always compare the calculator’s estimate with the dealer’s offer. If there’s a significant difference, ask the dealer to explain each component of their calculation.
Practical Example: Calculating a Car Lease
Let’s walk through a real-world example to demonstrate how an Auto Lease Calculator works:
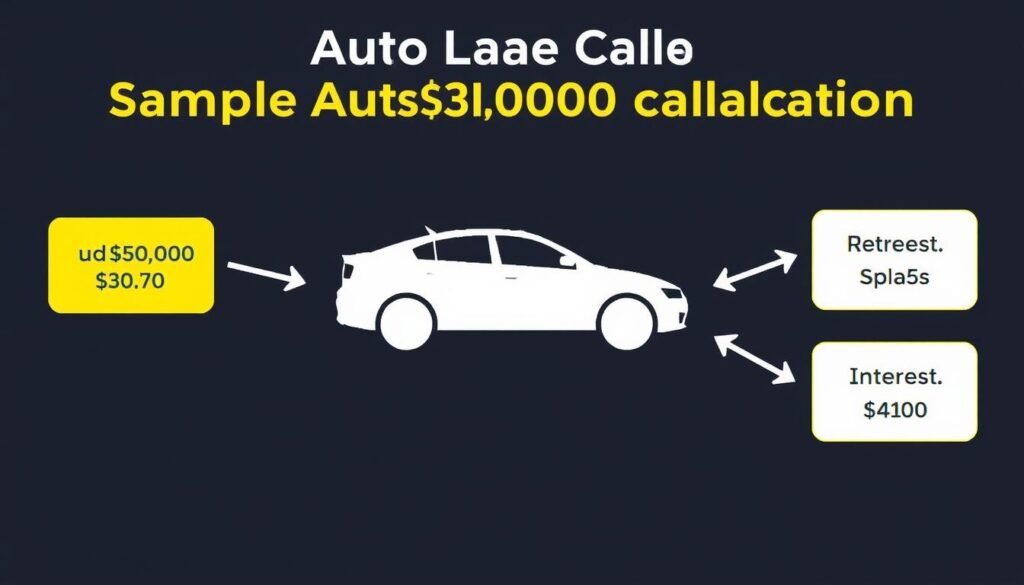
| Lease Component | Value |
| Vehicle Price (Negotiated) | $30,000 |
| Down Payment | $3,000 |
| Lease Term | 36 months |
| Residual Value (55%) | $16,500 |
| Money Factor | 0.00125 (3% APR) |
| Sales Tax Rate | 6% |
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Calculate the capitalized cost: $30,000 – $3,000 = $27,000
- Calculate depreciation: $27,000 – $16,500 = $10,500
- Monthly depreciation: $10,500 ÷ 36 = $291.67
- Monthly finance charge: ($27,000 + $16,500) × 0.00125 = $54.38
- Pre-tax monthly payment: $291.67 + $54.38 = $346.05
- Monthly tax: $346.05 × 0.06 = $20.76
- Total monthly payment: $346.05 + $20.76 = $366.81
This example shows how the various components combine to create your monthly lease payment. The Auto Lease Calculator performs these calculations automatically, saving you time and ensuring accuracy.
Ready to Calculate Your Own Lease?
Try our calculator with your specific numbers to see what your monthly payment would be.
Auto Lease Calculator
Use this calculator to estimate your monthly lease payments. Enter the required information below and click “Calculate” to see your results.
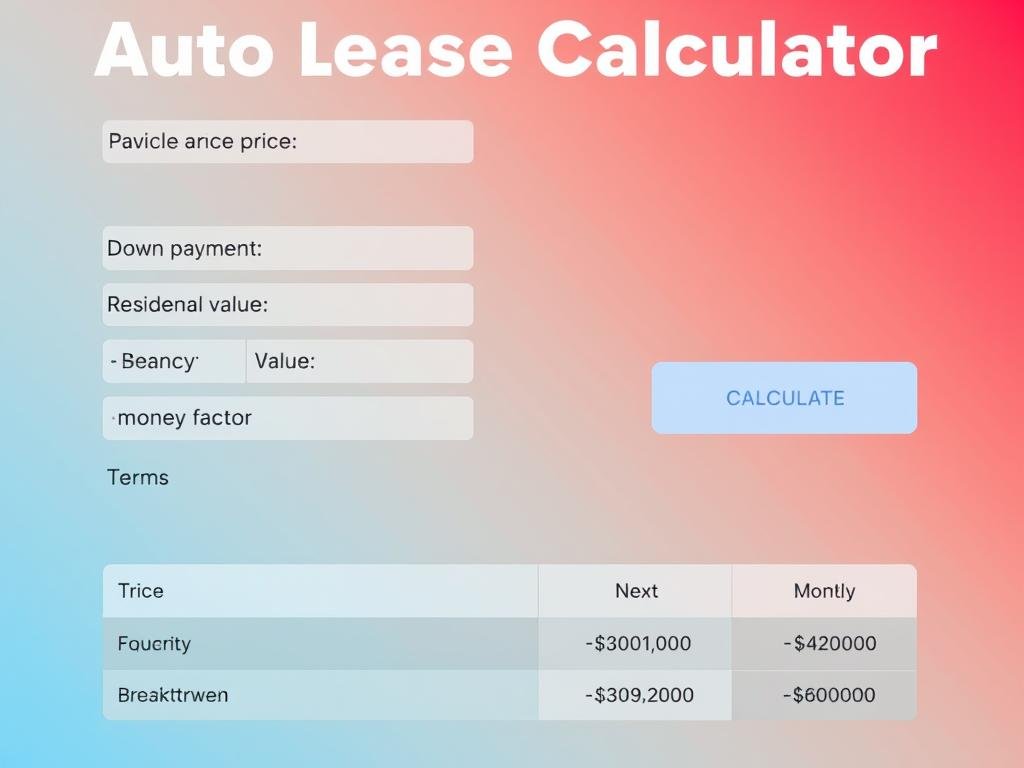
Lease Payment Results
| Monthly Lease Payment | $0.00 |
| Total Lease Cost | $0.00 |
| Total Depreciation | $0.00 |
| Total Interest | $0.00 |
Manual Calculation vs. Digital Auto Lease Calculators
While understanding the manual calculation process is valuable, digital Auto Lease Calculators offer significant advantages:

Benefits of Digital Calculators
- Instant calculations without manual math
- Ability to quickly adjust variables to see different scenarios
- Reduced chance of calculation errors
- Often include additional features like tax calculations
- Mobile accessibility for on-the-go comparisons at dealerships
Limitations of Manual Calculations
- Time-consuming and complex formulas
- Higher potential for mathematical errors
- Difficult to quickly compare multiple scenarios
- May not account for all variables (taxes, fees)
- Requires understanding of leasing formulas
While digital calculators are more convenient, understanding the manual calculation process helps you verify the accuracy of calculator results and better negotiate with dealers who may use different calculation methods.
Save Time with Our Digital Calculator
Skip the complex math and get instant results with our easy-to-use tool.
Popular Auto Lease Calculator Tools
Several reliable online Auto Lease Calculators are available to help you estimate your payments. Here’s an overview of the top options:

Calculator.net
Key Features:
- Comprehensive educational content
- Simple, user-friendly interface
- Detailed breakdown of payments
- Comparison with purchase options
NerdWallet
Key Features:
- Educational guides alongside calculator
- Money factor conversion tool
- Customizable mileage options
- Links to current lease offers
Edmunds
Key Features:
- Industry-specific residual values
- Current manufacturer incentives
- Dealer-specific pricing
- Comprehensive fee inclusion
Expert Tip: Use multiple calculators to cross-reference your results. Different calculators may use slightly different formulas or default values, so comparing results gives you a more accurate range of potential payments.
Common Mistakes When Calculating Lease Payments
Even with calculators, people often make mistakes that lead to inaccurate estimates. Here are the most common errors to avoid:
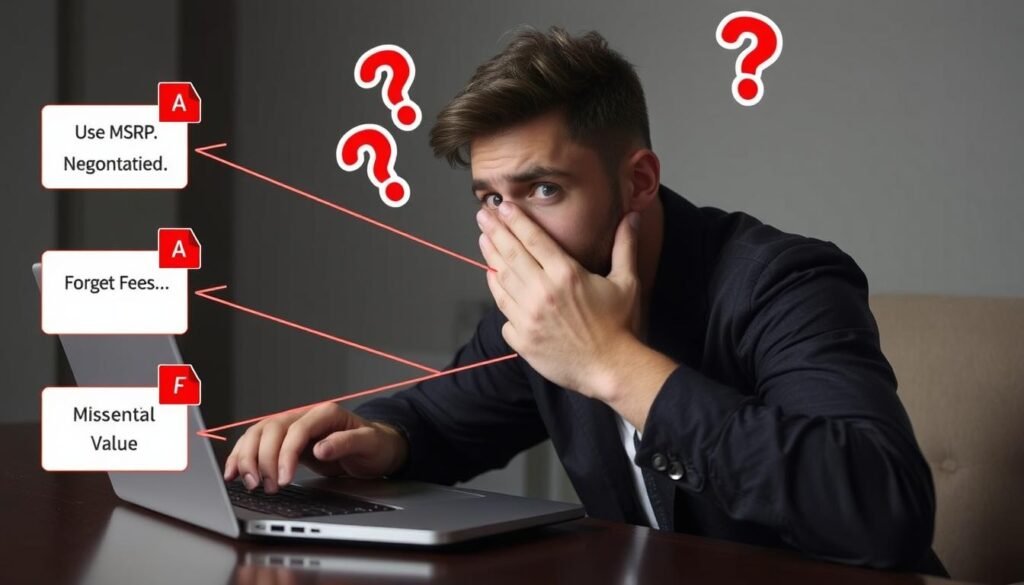

Common Mistakes
- Using MSRP instead of negotiated price
- Forgetting to include all fees and taxes
- Overestimating residual value
- Not accounting for money factor correctly
- Ignoring mileage limitations
- Overlooking acquisition and disposition fees
Best Practices
- Use the negotiated price as your capitalized cost
- Include all fees, taxes, and charges in calculations
- Research accurate residual values for your specific vehicle
- Convert APR to money factor correctly (divide by 2,400)
- Choose realistic mileage allowances based on your driving habits
- Factor in all lease-specific fees
Warning: Dealerships may present lease offers with unrealistically low mileage allowances or exclude certain fees to make monthly payments appear lower. Always ask for a complete breakdown of all costs.
Negotiation Tips Based on Calculator Results
Armed with information from an Auto Lease Calculator, you can negotiate more effectively at the dealership. Here’s how to leverage your knowledge:

- Negotiate the capitalized cost first: The vehicle’s price is the most negotiable aspect of a lease. Every dollar saved here reduces your monthly payment.
- Know the money factor: Dealers may mark up the money factor. Ask for the “buy rate” (the rate the leasing company charges the dealer) and negotiate from there.
- Question low residual values: If a dealer’s residual value seems low compared to industry averages, ask why or consider a different vehicle with better residual value.
- Beware of added fees: Challenge any fees that weren’t disclosed upfront or seem unusually high.
- Compare multiple offers: Use your calculator results to compare offers from different dealers.
- Focus on the total cost: Don’t be swayed by a low monthly payment if the total cost is high due to a large down payment or fees.
Always run the numbers through your calculator before signing. A dealer’s verbal promise of a “great deal” should be verified with actual calculations.
Prepare for Your Dealership Visit
Calculate your lease payments now so you can negotiate with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Auto Lease Calculations

Can I negotiate the residual value of a lease?
Unlike the capitalized cost, the residual value is typically set by the leasing company, not the dealer, and is generally non-negotiable. However, you can shop around for vehicles that naturally have higher residual values, which will result in lower monthly payments.
How does my credit score affect my lease calculation?
Your credit score primarily affects the money factor (interest rate) of your lease. Higher credit scores qualify for lower money factors, resulting in lower monthly payments. The difference between an excellent credit score and a poor one can amount to hundreds of dollars over the lease term.
Should I make a down payment on a lease?
Unlike buying a car, making a large down payment on a lease isn’t always advantageous. While it reduces your monthly payment, you don’t build equity in a leased vehicle. Additionally, if the car is totaled or stolen early in the lease, you typically won’t get your down payment back. Many financial experts recommend making only the minimum required down payment.
How accurate are online Auto Lease Calculators?
Online calculators provide good estimates but may not capture every fee or incentive that affects your actual lease payment. They’re most accurate when you have all the correct inputs, including the exact money factor, residual value, and all applicable fees. Use them as a guide, but expect some variation in the final numbers from the dealer.
Can I use an Auto Lease Calculator for used cars?
Yes, you can use an Auto Lease Calculator for used cars, but you’ll need accurate information about the used car’s current value and projected residual value. Used car leases are less common and may have different terms than new car leases, including higher money factors and lower residual values.
Still Have Questions?
Try our calculator to see how different factors affect your lease payment.
Making Informed Leasing Decisions
An Auto Lease Calculator is an invaluable tool for anyone considering leasing a vehicle. By understanding how lease calculations work and using these calculators effectively, you can:

- Estimate your monthly payments accurately before visiting a dealership
- Compare different vehicles and lease terms to find the best option
- Identify potentially unfavorable lease terms
- Negotiate more effectively with dealers
- Avoid unexpected costs and surprises
Remember that while the monthly payment is important, it’s just one aspect of a lease agreement. Consider the total cost of leasing, including down payment, monthly payments, and end-of-lease fees. Also factor in practical considerations like mileage allowance and wear-and-tear policies.
By combining the power of an Auto Lease Calculator with a thorough understanding of leasing terms, you’ll be well-equipped to secure a lease that fits your budget and driving needs.
Ready to Calculate Your Lease?
Use our calculator to get started on your leasing journey.