Choosing the right size heating or cooling system is crucial for comfort and efficiency. Too small, and your system struggles to maintain temperature. Too large, and you waste energy with constant cycling. Our BTU calculator helps you find that perfect balance for optimal performance and energy savings.
Ready to find your perfect system size?
Skip the guesswork and get an accurate BTU calculation based on your specific space.

What is a BTU?
A BTU (British Thermal Unit) is the standard measurement used to determine the heating and cooling capacity of HVAC systems. By definition, one BTU is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
When shopping for air conditioners, heaters, or other climate control systems, you’ll see BTU ratings that indicate how much heating or cooling power the unit provides per hour. For cooling systems, this number represents how much heat the unit can remove from a room. For heating systems, it shows how much heat the unit can generate.

1 BTU equals approximately 1,055 joules, 252 calories, or 0.293 watt-hours. For perspective, the energy released by burning one match is roughly equivalent to 1 BTU.
Why BTU Calculation is Important
Selecting a system with the correct BTU rating is essential for several reasons:
Undersized Systems
- Run constantly without reaching desired temperature
- Increase energy bills due to continuous operation
- Wear out faster from overuse
- Leave spaces uncomfortable, especially during extreme weather
- May lead to humidity problems in cooling applications
Oversized Systems
- Cycle on and off frequently (short-cycling)
- Create temperature fluctuations and uneven comfort
- Consume more energy than necessary
- Wear out components faster due to frequent starting/stopping
- Cost more upfront with no benefit
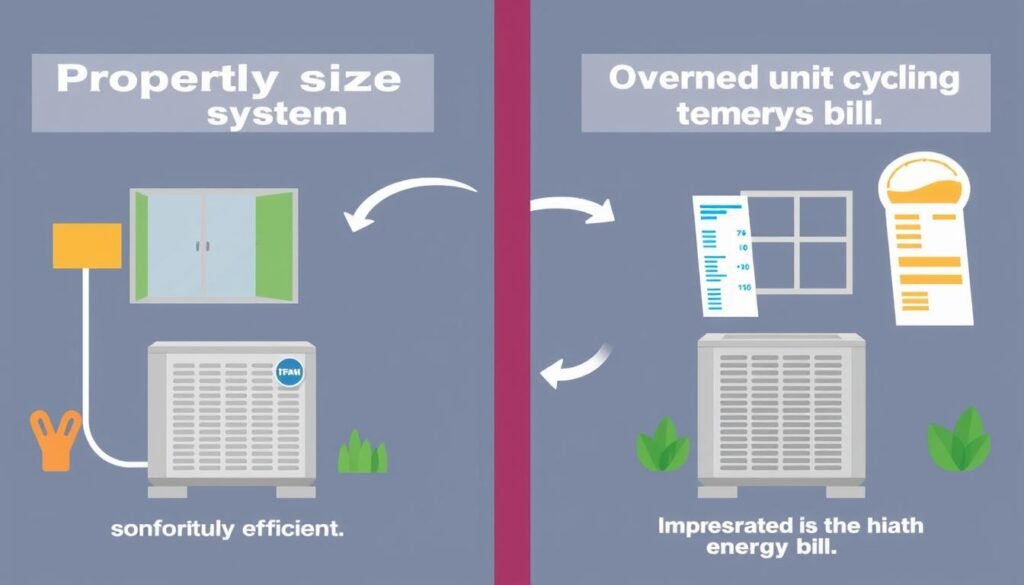
Don’t risk comfort or efficiency
Avoid costly mistakes by determining the exact BTU requirements for your space.
Factors Affecting BTU Requirements
Several key factors influence how many BTUs you’ll need to effectively heat or cool your space:
Square Footage
The most fundamental factor is the size of your space. As a basic rule of thumb, you’ll need approximately 20 BTUs per square foot for cooling and 20-40 BTUs per square foot for heating, depending on your climate zone.
| Area (Square Feet) | Approximate Cooling BTUs | Approximate Heating BTUs (Moderate Climate) |
| 100-150 | 5,000 | 3,000-6,000 |
| 150-250 | 6,000 | 6,000-10,000 |
| 250-300 | 7,000 | 10,000-12,000 |
| 300-350 | 8,000 | 12,000-14,000 |
| 350-400 | 9,000 | 14,000-16,000 |
| 400-450 | 10,000 | 16,000-18,000 |
| 450-550 | 12,000 | 18,000-22,000 |
Ceiling Height
Standard BTU calculations assume ceiling heights of 8-9 feet. For higher ceilings, you’ll need to adjust your BTU requirements upward. For each foot above 8 feet, add approximately 15% to your BTU calculation.
Climate Zone
Your geographical location significantly impacts BTU needs. Homes in colder climates require more heating BTUs, while those in hotter regions need more cooling capacity.
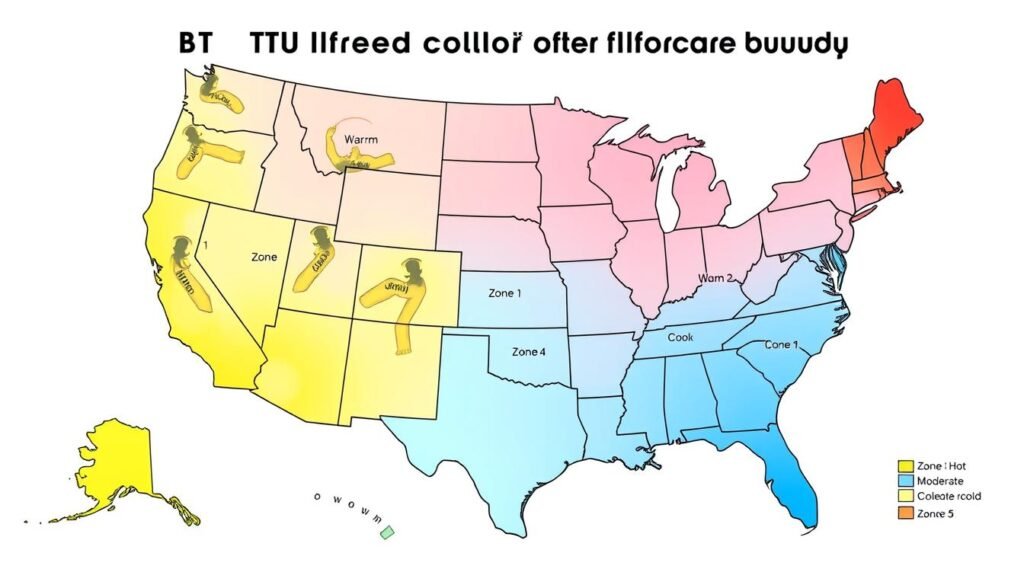
Insulation Quality
The quality of your home’s insulation dramatically affects energy efficiency and BTU requirements:
Poor Insulation
Older homes (pre-1980s), single-pane windows, visible gaps around doors/windows
Add 30-40% more BTUs
Average Insulation
Standard construction, double-pane windows, basic weather stripping
Standard BTU calculation
Excellent Insulation
Energy-efficient homes, triple-pane windows, proper sealing, added insulation
Reduce BTUs by 10-15%
Sun Exposure
Rooms with significant sun exposure through windows may need 10-15% more cooling BTUs. South and west-facing rooms typically receive more direct sunlight in the Northern Hemisphere.
Room Usage
Different rooms have different heating and cooling needs based on their typical use:
- Kitchens: Add 4,000 BTUs to account for heat-generating appliances
- Living rooms: Add 1,000 BTUs per person who regularly occupies the space
- Computer rooms: Add 1,200 BTUs to account for electronic equipment

Number of Occupants
Each person in a room generates approximately 600 BTUs of heat per hour. For spaces regularly occupied by multiple people, add this to your calculations.
Windows and Doors
Windows and exterior doors can significantly impact heat transfer:
- Add 1,000 BTUs for each standard window
- Add 1,500 BTUs for each large window (over 6 feet)
- Add 1,000 BTUs for each exterior door
Too many factors to calculate manually?
Our BTU calculator takes all these variables into account automatically.
How to Use a BTU Calculator
While our online calculator handles the complex math automatically, understanding the process helps you appreciate the factors involved:
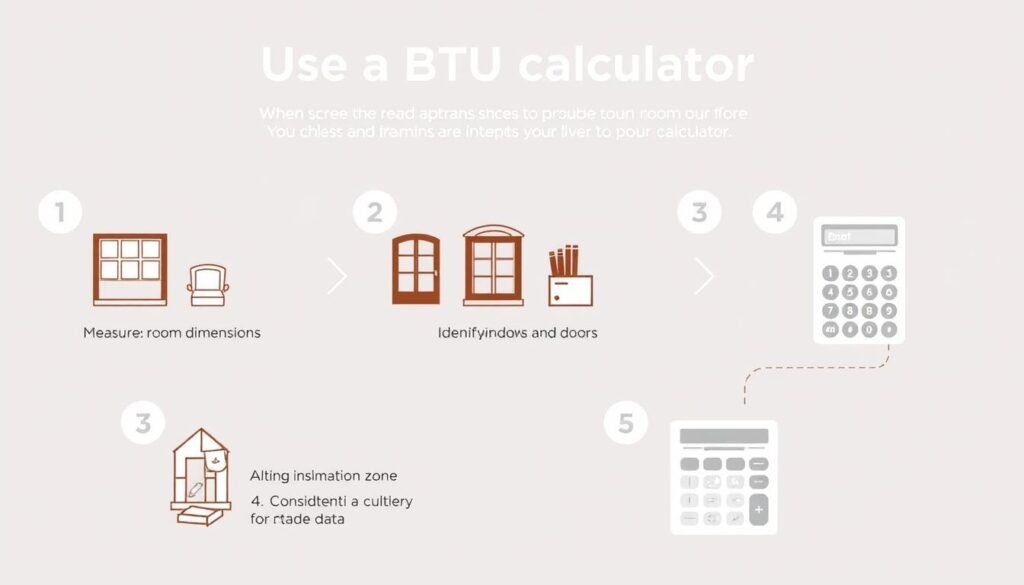
Basic Calculation Process
- Measure the square footage of your space (length × width)
- Determine your climate zone from the map
- Assess your insulation quality (poor, average, excellent)
- Count windows and exterior doors
- Consider ceiling height, sun exposure, and room usage
- Apply the appropriate multipliers to your base square footage calculation
Sample BTU Calculations
Example 1: Small Bedroom
Room details:
- Dimensions: 10ft × 12ft = 120 square feet
- Climate zone: Moderate (Zone 3)
- Insulation: Average
- Windows: 1 standard window
- Ceiling height: 8ft (standard)
Calculation:
Base BTU: 120 sq ft × 20 BTUs = 2,400 BTUs
Add for window: +1,000 BTUs
Total: 3,400 BTUs
Recommended air conditioner size: 5,000 BTUs (nearest standard size)
Example 2: Sunny Living Room
Room details:
- Dimensions: 15ft × 20ft = 300 square feet
- Climate zone: Warm (Zone 2)
- Insulation: Poor (older home)
- Windows: 3 large windows with western exposure
- Ceiling height: 10ft (higher than standard)
- Occupants: Family of 4 regularly uses this room
Calculation:
Base BTU: 300 sq ft × 20 BTUs = 6,000 BTUs
Poor insulation adjustment: +30% = +1,800 BTUs
High ceiling adjustment: +15% = +900 BTUs
Windows: 3 large windows × 1,500 BTUs = +4,500 BTUs
Sun exposure: +15% = +900 BTUs
Occupants: 4 people × 600 BTUs = +2,400 BTUs
Total: 16,500 BTUs
Recommended air conditioner size: 18,000 BTUs (nearest standard size)
Example 3: Open Kitchen/Dining Area
Room details:
- Dimensions: 14ft × 25ft = 350 square feet
- Climate zone: Cold (Zone 5)
- Insulation: Excellent (recently renovated)
- Windows: 2 standard windows
- Ceiling height: 9ft
- Kitchen appliances: Standard range, refrigerator, dishwasher
Calculation:
Base BTU (heating): 350 sq ft × 40 BTUs = 14,000 BTUs
Excellent insulation adjustment: -15% = -2,100 BTUs
Windows: 2 standard windows × 1,000 BTUs = +2,000 BTUs
Kitchen appliances: +4,000 BTUs
Total: 17,900 BTUs
Recommended heater size: 18,000 BTUs (nearest standard size)

System Efficiency Considerations
Remember that BTU ratings on heating and cooling equipment refer to energy input, not output. System efficiency affects how much of that energy actually heats or cools your space:
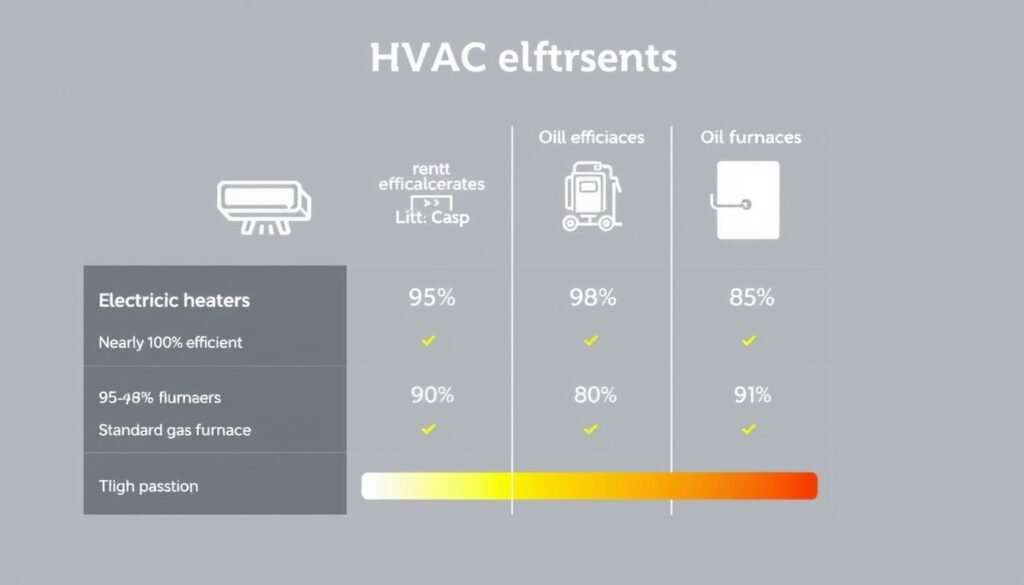
- Electric heaters: Nearly 100% efficient (all energy converts to heat)
- High-efficiency gas furnaces: 90-98% efficient
- Standard gas furnaces: 80-85% efficient
- Oil furnaces: 80-90% efficient
- Air conditioners: Efficiency measured by SEER rating (higher is better)
For example, if you need 20,000 BTUs of heat and your furnace is 80% efficient, you’ll need a furnace rated for 25,000 BTUs (20,000 ÷ 0.8 = 25,000).
Finding Your Perfect BTU Size
Determining the right BTU size for your heating and cooling needs doesn’t have to be complicated. While this guide provides the fundamentals of BTU calculation, our online calculator makes the process simple and accurate.
Remember that proper sizing is an investment in comfort, efficiency, and equipment longevity. An appropriately sized system will maintain consistent temperatures, operate efficiently, and provide years of reliable service.

Ready to find your perfect BTU size?
Our calculator takes all the guesswork out of sizing your heating and cooling system.