Circle Calculator helps you find area, radius, diameter, and circumference instantly. Quick, accurate, and easy tool for geometry and math problems.
Circle Calculator
Our Circle Calculator provides instant calculations for any circle's area, circumference, radius, and diameter. Whether you're a student working on geometry homework, an engineer designing circular components, or a DIY enthusiast planning a project, this tool eliminates the need for manual calculations and potential errors. Simply input one known value, and our calculator will determine all other measurements automatically.
In this guide, we'll explain all circle properties, provide the essential formulas, and show you how to calculate these values manually. You'll also discover practical applications for circle calculations in everyday life and professional settings.
Understanding Circle Basics
Basic elements of a circle: radius, diameter, circumference, and area
A circle is a perfectly round shape where every point on its edge is the same distance from the center point. This constant distance is called the radius. Understanding the relationship between a circle's radius, diameter, circumference, and area is essential for performing accurate calculations.
Key Circle Properties
- Radius (r): The distance from the center to any point on the circle's edge
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle through its center (d = 2r)
- Circumference (C): The total distance around the circle (C = 2πr or C = πd)
- Area (A): The space contained within the circle (A = πr²)
- Center: The point inside the circle that is equidistant from all points on the edge
The Importance of Pi (π)
Pi (π) is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. It's approximately equal to 3.14159, though it's an irrational number with infinite non-repeating digits. For most calculations, using 3.14 or 3.142 provides sufficient accuracy.
Pi is essential for all circle calculations and appears in both the circumference and area formulas.
Need Quick Circle Calculations?
Skip the manual work and get instant results with our free Circle Calculator tool.
Essential Circle Formulas
These fundamental formulas allow you to calculate any circle measurement when you know at least one value. Our Circle Calculator uses these same formulas to provide instant results.
Diameter Formula
If you know the radius:
d = 2r
If you know the circumference:
d = C/π
If you know the area:
d = 2√(A/π)
Radius Formula
If you know the diameter:
r = d/2
If you know the circumference:
r = C/(2π)
If you know the area:
r = √(A/π)
Circumference Formula
If you know the radius:
C = 2πr
If you know the diameter:
C = πd
If you know the area:
C = 2π√(A/π)

Area of a Circle Formula
The area of a circle represents the space contained within its boundary. The formula for calculating a circle's area is:
A = πr²
If you know the diameter instead of the radius, you can use:
A = π(d/2)² or A = πd²/4
If you know the circumference, you can calculate the area using:
A = C²/(4π)
Step-by-Step Calculation Examples
Let's walk through some practical examples of how to manually calculate different circle measurements. These examples will help you understand how to apply the formulas correctly.
Example 1: Finding Circumference from Radius
Problem: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Step 1: Identify the formula for circumference when radius is known.
C = 2πr
Step 2: Substitute the radius value into the formula.
C = 2π × 5 cm
Step 3: Calculate (using π ≈ 3.14).
C = 2 × 3.14 × 5 cm
C = 31.4 cm
Answer: The circumference of the circle is 31.4 cm.
Example 2: Finding Area from Diameter
Problem: Calculate the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 inches.
Step 1: Convert diameter to radius.
r = d/2 = 10/2 = 5 inches
Step 2: Apply the area formula.
A = πr²
A = π × 5² = π × 25
Step 3: Calculate (using π ≈ 3.14).
A = 3.14 × 25 = 78.5 square inches
Answer: The area of the circle is 78.5 square inches.
Example 3: Finding Radius from Area
Problem: Find the radius of a circle with an area of 200 square meters.
Step 1: Start with the area formula and solve for radius.
A = πr²
r² = A/π
r = √(A/π)
Step 2: Substitute the area value.
r = √(200/π)
Step 3: Calculate (using π ≈ 3.14).
r = √(200/3.14) = √63.69 = 7.98 meters
Answer: The radius of the circle is approximately 7.98 meters.

Save Time on Calculations
Our Circle Calculator handles all these calculations instantly. Just enter one value to find all circle measurements.
Real-World Applications of Circle Calculations
Circle calculations are essential in numerous fields and everyday situations. Here are some common applications where our Circle Calculator can be particularly useful:
Construction & Engineering
- Designing circular foundations, pillars, and structures
- Calculating material requirements for pipes and cylindrical components
- Planning circular rooms, domes, and architectural features
- Determining spacing for circular arrangements (like columns)
Education & Mathematics

- Solving geometry problems and homework assignments
- Teaching fundamental mathematical concepts
- Preparing for math exams and standardized tests
- Demonstrating the practical applications of π (pi)
DIY & Home Projects

- Designing circular garden beds and landscaping features
- Building round tables, fire pits, or decorative elements
- Calculating fabric needed for circular items (tablecloths, rugs)
- Planning space for circular furniture arrangements
Additional Applications
Science & Technology
- Calculating orbital paths in astronomy
- Determining lens specifications in optics
- Designing circular components in electronics
- Analyzing circular motion in physics
Arts & Crafts
- Creating circular artwork and designs
- Determining material needs for circular frames
- Designing circular patterns for quilting and sewing
- Planning circular mosaics and decorative pieces

How to Find the Center of a Circle
Finding the center of an existing circle is a common practical problem. Here are two reliable methods you can use:
Method 1: Using Perpendicular Bisectors
- Draw any two chords (straight lines connecting two points on the circle)
- Find the midpoint of each chord
- Draw perpendicular lines through these midpoints
- The point where these perpendicular lines intersect is the center of the circle

Method 2: Using Right Angles
- Place a right-angled object (like a carpenter's square) so that it touches the circle at any point
- Draw two perpendicular lines across the circle from this point
- Mark where these lines intersect the circle on the opposite sides
- Connect these points to create a diameter
- Repeat with another point to create a second diameter
- The intersection of these diameters is the center of the circle
Finding the center of a circle is essential for many practical applications, including construction, design, and crafts. Once you've found the center, you can accurately measure the radius and calculate other circle properties.
Special Types of Circles
Beyond the basic circle, there are several special types and related concepts that are important in mathematics and practical applications:
Unit Circle
A circle with a radius of 1 unit, typically centered at the origin (0,0) on a coordinate plane. The unit circle is fundamental in trigonometry and calculus.
On the unit circle, for any point (x,y):
- x = cos θ
- y = sin θ
- x² + y² = 1
Concentric Circles
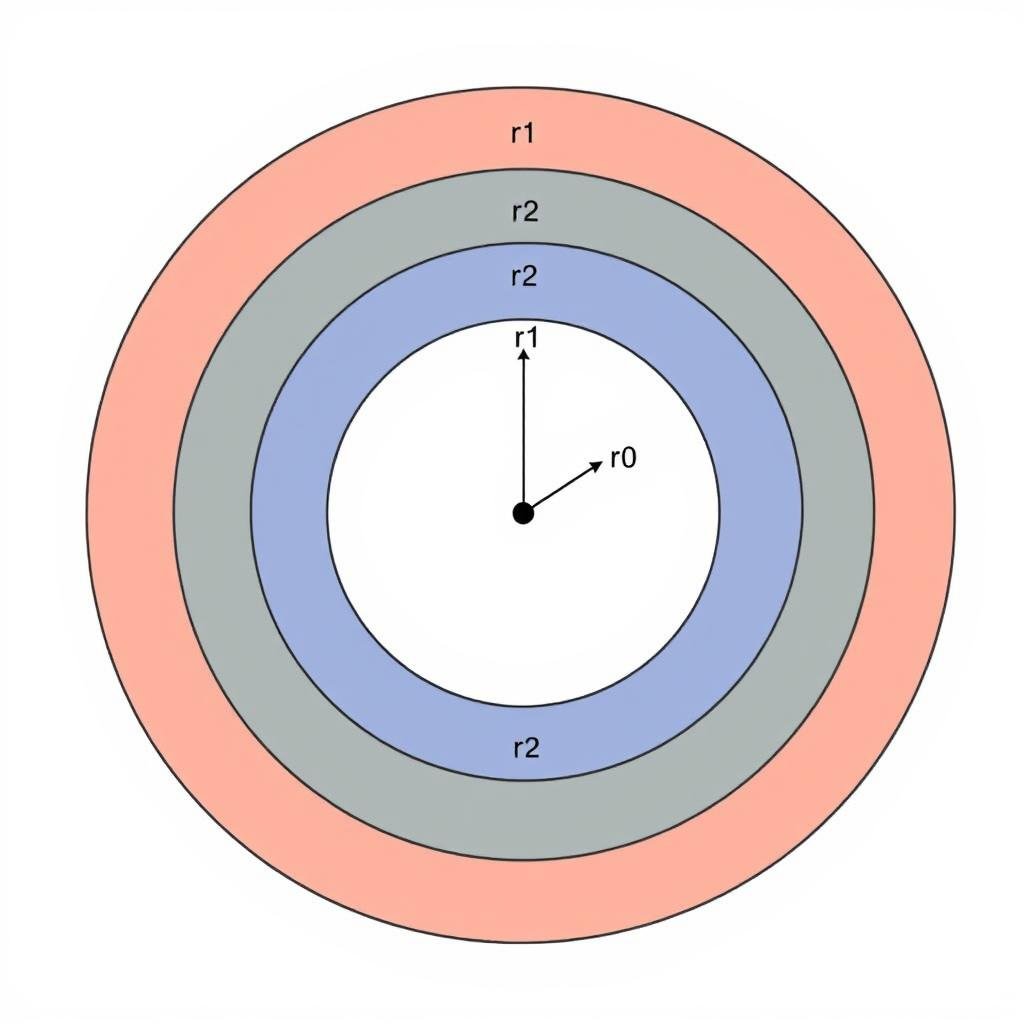
Circles that share the same center point but have different radii. The space between two concentric circles is called an annulus.
Examples in real life include:
- Tree rings
- Archery targets
- Ripples in water
- Vinyl record grooves
Circle Segments & Sectors
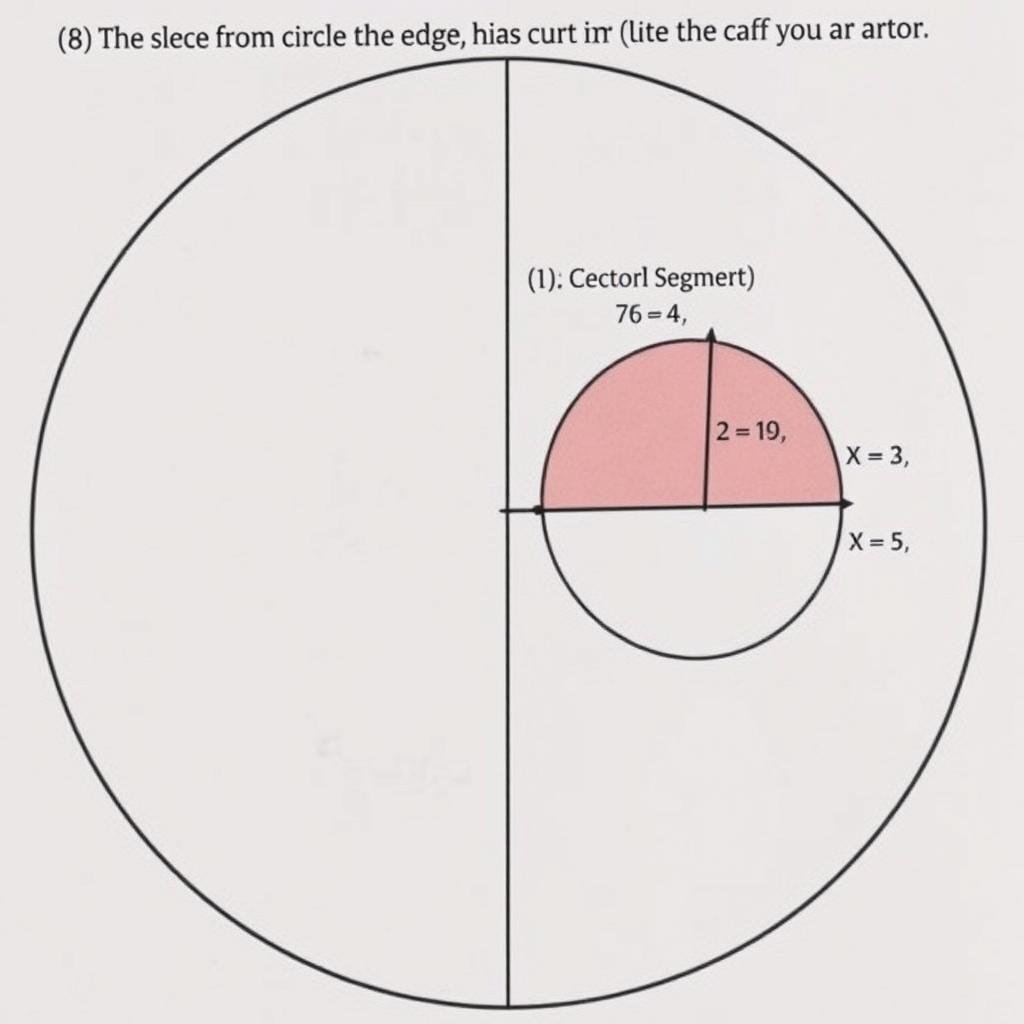
A sector is a "pie slice" of a circle. A segment is the area bounded by an arc and a chord.
For a sector with angle θ (in radians):
- Area = (θ/2)r²
- Arc length = rθ
Why Use Our Circle Calculator?
While understanding how to manually calculate circle measurements is valuable, our Circle Calculator offers several advantages:
Benefits of Using Our Calculator
- Instant results without manual calculations
- Eliminates potential math errors
- Calculates all circle measurements from just one input
- Handles complex calculations with perfect accuracy
- Saves time on homework, projects, and professional tasks
- Converts between different units of measurement
- Free to use with no registration required
Whether you're a student learning geometry, a professional working on designs, or someone tackling a DIY project, our Circle Calculator provides the accuracy and convenience you need for all circle-related calculations.
Ready to Calculate Circle Measurements?
Try our free Circle Calculator now and get instant, accurate results for any circle problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between circumference and perimeter?
Circumference is the specific term used for the perimeter of a circle. While "perimeter" refers to the total length of the boundary of any shape, "circumference" is used exclusively for the distance around a circle.
Can the area and circumference of a circle be equal?
Yes, the area and circumference of a circle can be equal when the radius is exactly 2 units. When r = 2, the area is πr² = 4π, and the circumference is 2πr = 4π. Remember that the units would be different (square units for area, linear units for circumference).
How accurate is the value of π used in calculations?
For most practical purposes, using π ≈ 3.14 or 3.142 provides sufficient accuracy. Our calculator uses a more precise value of π for calculations. Mathematically, π is an irrational number with an infinite number of non-repeating decimal places.
What is the formula for finding the diameter when only the area is known?
To find the diameter when only the area is known, use the formula: d = 2√(A/π), where A is the area and π is approximately 3.14159.