Welcome to our comprehensive guide on dice rollers, the digital evolution of physical dice that brings random number generation to your fingertips. Whether you’re a tabletop gaming enthusiast, an educator, or someone who needs to make random decisions, understanding how virtual dice work can enhance your experience. This guide explores everything from basic dice concepts to advanced applications, providing you with valuable insights into the world of digital dice rolling.

Various polyhedral dice used in tabletop gaming and virtual dice rollers
What is a Dice Roller?
A dice roller is a digital tool that simulates the rolling of physical dice, generating random numbers within specified ranges. Unlike traditional physical dice that rely on physics and gravity to produce random results, virtual dice rollers use mathematical algorithms called random number generators (RNGs) to create unpredictable outcomes.
The concept of dice has evolved from ancient civilizations where knucklebones and carved cubes were used for games of chance and divination. Today’s virtual dice roller maintains the spirit of those early random number generators while offering enhanced convenience and versatility.
Modern dice rollers can simulate any type of die with any number of faces, from the common six-sided cube to specialized polyhedral dice with 4, 8, 10, 12, or 20 faces. This flexibility makes them invaluable for various applications beyond traditional gaming.

Explore Our Math Calculators
Discover our collection of probability and statistics calculators to further understand the mathematics behind random events.
Why Use an Online Dice Roller?
Virtual dice rollers offer numerous advantages over physical dice, making them an excellent choice for many situations. Understanding these benefits can help you decide when to use a digital dice roller versus traditional dice.
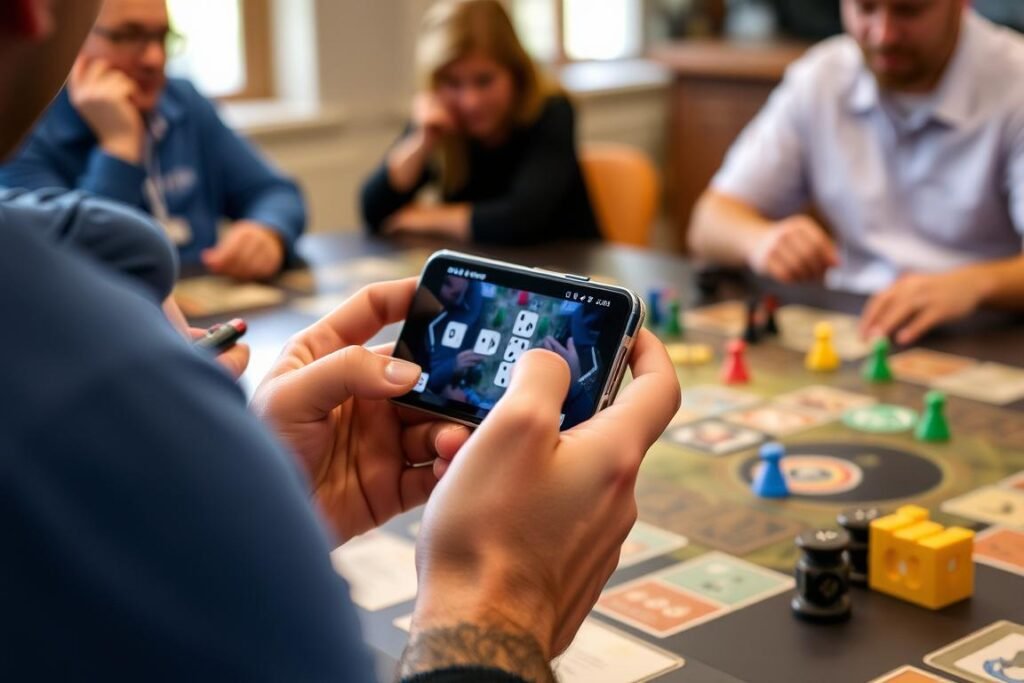

Digital dice rollers provide convenience during tabletop gaming sessions
Convenience
Access dice rolling functionality anytime, anywhere without carrying physical dice. Perfect for impromptu gaming sessions or when physical dice are unavailable.
Versatility
Roll any combination of dice with any number of faces, including unconventional dice that may be difficult to find physically. Combine multiple dice types in a single roll.
Fairness
Modern random number generators provide results that are statistically random, eliminating concerns about weighted or imperfect physical dice affecting outcomes.
Speed
Generate results instantly, even for complex dice combinations that would take time to roll and calculate manually. Ideal for games requiring frequent or numerous dice rolls.
Accessibility
Enable people with mobility limitations to participate fully in dice-based games without physical manipulation of dice. Also useful in space-constrained environments.
Record Keeping
Many online dice rollers automatically log results, allowing players to review previous rolls and maintain a history of game events for reference.
While physical dice offer tactile satisfaction and tradition, virtual dice rollers provide practical solutions for many modern gaming and decision-making scenarios. The choice between physical and virtual dice often comes down to personal preference and specific situational needs.
Common Types of Dice
Dice come in various shapes and sizes, each with a specific number of faces. Understanding the different types of dice and their common uses can help you select the right dice for your specific needs. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the most common polyhedral dice used in tabletop gaming and virtual dice rollers:
| Die Type | Shape | Common Uses |
| d4 (Four-sided) | Tetrahedron | Small damage rolls, minor effects, dagger damage in D&D |
| d6 (Six-sided) | Cube | Standard die for most board games, attribute checks, medium weapon damage |
| d8 (Eight-sided) | Octahedron | Medium weapon damage, spell effects, hit points for certain classes |
| d10 (Ten-sided) | Pentagonal trapezohedron | Percentile rolls (with another d10), damage for larger weapons |
| d12 (Twelve-sided) | Dodecahedron | Larger weapon damage, special abilities, barbarian hit points |
| d20 (Twenty-sided) | Icosahedron | Attack rolls, saving throws, skill checks, core mechanic in D&D |
| d100 (Hundred-sided) | Two d10s (percentile) | Percentage checks, random tables, critical hit effects |

Various polyhedral dice showing their distinctive shapes and number of faces
Specialized and Uncommon Dice
Beyond the standard polyhedral dice, there are several specialized and uncommon dice types that serve specific purposes:
- Fate/Fudge Dice: Six-sided dice with two plus faces, two minus faces, and two blank faces, used in the FATE roleplaying system.
- Double Dice: Dice within dice that allow for two random numbers in one roll.
- Custom Dice: Dice with symbols, words, or special markings instead of numbers, often used in specific board games.
- Weighted Dice: Unfair dice designed to favor certain outcomes (used for magic tricks or cheating).

Explore Our Gaming Calculators
Enhance your gaming experience with our specialized calculators designed for tabletop RPGs and board games.
Applications of a Dice Roller
While dice rollers are commonly associated with tabletop gaming, their utility extends far beyond entertainment. The ability to generate random numbers quickly and fairly makes dice rollers valuable tools in numerous fields and activities.
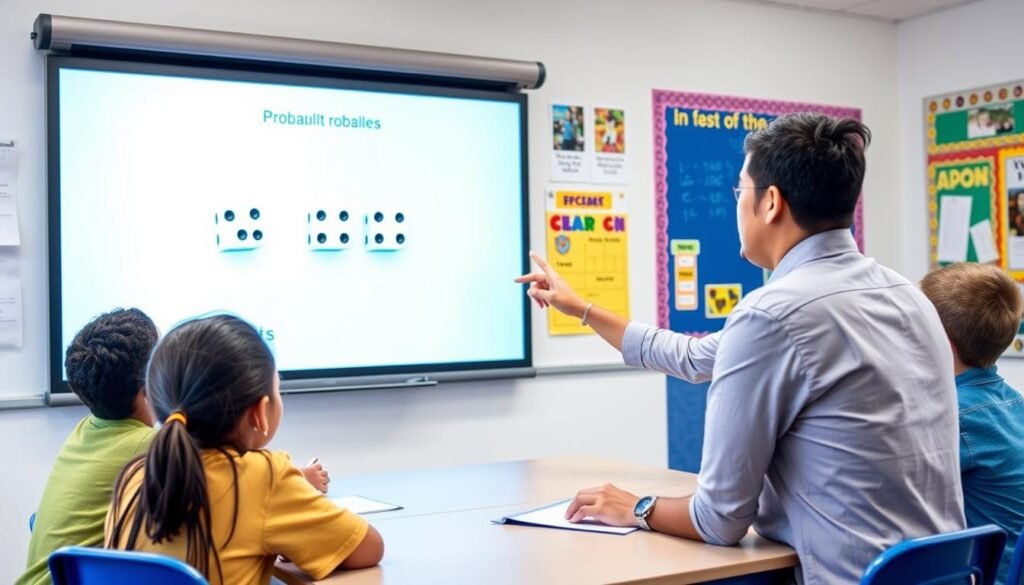

Educational applications of dice rollers for teaching probability and mathematics
Gaming Applications
The most obvious use of dice rollers is in gaming contexts:
- Tabletop RPGs: Games like Dungeons & Dragons, Pathfinder, and Call of Cthulhu rely heavily on dice rolls for determining outcomes of actions, combat, and skill checks.
- Board Games: Many board games use dice for movement, resource generation, or resolving conflicts.
- Wargaming: Miniature wargames often require numerous dice rolls to resolve combat between units.
- Game Development: Game designers use dice rollers to test probability distributions and balance game mechanics.

Educational Applications

Dice rollers serve as excellent educational tools:
- Mathematics Education: Teaching probability, statistics, and data analysis through practical demonstrations.
- Science Experiments: Generating random samples or simulating random events in scientific studies.
- Language Learning: Creating random prompts for vocabulary practice or conversation starters.
- Classroom Management: Randomly selecting students for participation or assigning groups.
Practical Real-World Applications
Decision Making
When faced with equally valid options, a dice roll can provide an unbiased method for making decisions, from choosing restaurants to resolving minor disputes.
Creative Inspiration
Writers, artists, and musicians use random generators to overcome creative blocks, generate story prompts, or explore new creative directions.
Software Testing
Developers use random number generation to test software under various conditions and ensure robust performance with unexpected inputs.

Using random number generation for professional research and statistical sampling
The versatility of dice rollers makes them valuable tools across numerous domains. Whether you’re a game master running an epic campaign, a teacher explaining probability, or a professional making randomized selections, a reliable dice roller can be an essential part of your toolkit.
How Our Dice Roller Works
Understanding the mechanics behind virtual dice rollers can help you appreciate their reliability and fairness. While physical dice rely on physics and the laws of motion, digital dice rollers employ sophisticated algorithms to generate random results.

Conceptual visualization of random number generation algorithms used in virtual dice rollers
Random Number Generation
At the heart of every dice roller is a random number generator (RNG). These mathematical algorithms produce sequences of numbers that appear random and unpredictable. There are two main types of RNGs used in dice rollers:
Pseudo-Random Number Generators (PRNGs)
Most dice rollers use PRNGs, which are algorithms that generate sequences of numbers that approximate true randomness. They start with a seed value (often derived from the current time) and apply mathematical transformations to produce seemingly random numbers.
While not truly random in the strictest sense (as they follow deterministic algorithms), modern PRNGs are sophisticated enough to produce results that are statistically indistinguishable from true randomness for most practical purposes.
True Random Number Generators (TRNGs)
Some advanced dice rollers may use TRNGs, which derive randomness from physical processes like atmospheric noise, radioactive decay, or quantum phenomena. These provide true randomness but are more complex to implement.
For most gaming and educational applications, well-designed PRNGs provide more than sufficient randomness to ensure fair and unpredictable results.
Ensuring Fairness
Quality dice rollers implement several measures to ensure the fairness and integrity of random rolls:
- Uniform Distribution: Each possible outcome has an equal probability of occurring. A d6 has exactly a 1/6 chance of rolling any number from 1 to 6.
- Independence: Each roll is completely independent of previous rolls, with no “memory” of past results.
- Unpredictability: Results cannot be predicted in advance, even with knowledge of the system.
- Statistical Testing: Good RNGs undergo rigorous statistical testing to verify their randomness properties.
Statistical distribution of results from 1000 virtual d20 dice rolls showing uniform probability
From Algorithm to Roll
When you use a virtual dice roller, here’s what typically happens behind the scenes:
- You select the type and number of dice to roll (e.g., 3d6 for three six-sided dice).
- The system generates a seed value, often based on the current millisecond timestamp.
- The RNG algorithm processes this seed to generate random numbers within the specified range (e.g., 1-6 for a d6).
- For multiple dice, this process repeats for each die, and the results may be summed or presented individually.
- The results are displayed to you, often with visual animations to simulate physical dice rolling.
Explore Our Probability Calculators
Interested in the mathematics behind randomness? Check out our probability calculators to explore statistical concepts further.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about virtual dice rollers and their applications.
Are online dice rollers truly random?
Most online dice rollers use pseudo-random number generators (PRNGs) that produce statistically random results suitable for gaming and educational purposes. While not “truly random” in the strictest mathematical sense, modern algorithms create sequences that are practically indistinguishable from true randomness for everyday use. High-quality dice rollers undergo statistical testing to ensure fair and uniform distribution of results.
Can I roll multiple dice at once?
Yes, most virtual dice rollers allow you to roll multiple dice simultaneously. You can typically specify both the number and type of dice using standard notation like “3d6” (three six-sided dice) or “2d20” (two twenty-sided dice). Some advanced dice rollers also allow complex combinations like “2d6+1d8+3” for tabletop RPG calculations.
What is the most common dice roll in tabletop games?
The most common dice roll varies by game system. In traditional board games, the d6 (six-sided die) is most prevalent. In Dungeons & Dragons and similar RPGs, the d20 is the core mechanic for determining success or failure of most actions. For damage calculations in RPGs, combinations of dice like 2d6, 1d8, or 3d6 are commonly used depending on the weapon or spell.
Are virtual dice rollers better than physical dice?
Neither is objectively “better” – they serve different purposes and preferences. Virtual dice rollers offer convenience, speed, and consistent randomness. They’re excellent for complex calculations, remote play, or situations where physical dice are impractical. Physical dice provide tactile satisfaction and tradition that many players enjoy. Many tabletop gamers use both, depending on the situation.
Can dice rollers be used for serious statistical applications?
Basic dice rollers are suitable for educational demonstrations and simple random sampling. However, for serious scientific or statistical applications, specialized software with well-documented random number generation algorithms is preferable. Professional statistical packages implement more sophisticated randomization techniques with proven mathematical properties suitable for research.

Using a virtual dice roller during an online tabletop gaming session
Conclusion
Virtual dice rollers represent the perfect blend of ancient randomization concepts and modern technology. From their humble origins as tools for tabletop gaming, they’ve evolved into versatile utilities with applications spanning education, creative arts, decision-making, and professional fields.
Whether you’re a dungeon master guiding players through epic adventures, a teacher explaining probability concepts, or simply someone who needs to make random selections, a reliable dice roller is an invaluable tool in your digital arsenal.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect dice rollers to become even more sophisticated, with enhanced visualizations, improved randomization algorithms, and greater integration with other digital tools. Yet at their core, they’ll continue to serve the fundamental human need for fair and unpredictable random outcomes.
Explore Our Full Calculator Collection
Discover our comprehensive suite of calculators designed to help with mathematics, finance, health, and everyday problem-solving.