Understanding and calculating the mass of objects is fundamental in physics, engineering, and everyday applications. Our Mass Calculator provides a simple way to determine an object’s mass using its density and volume. Whether you’re a student working on physics problems, an engineer designing components, or simply curious about the physical properties of objects, this comprehensive guide will help you understand mass calculations and how to apply them effectively.
What is Mass?

Mass is a fundamental property of matter that measures the amount of substance an object contains. Unlike weight, which varies depending on gravitational force, mass remains constant regardless of location. It represents an object’s resistance to acceleration when a force is applied, as described by Newton’s Second Law of Motion.
The standard unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) is the kilogram (kg). Other common units include grams (g), milligrams (mg), pounds (lb), and ounces (oz). Understanding mass is crucial for various scientific disciplines and practical applications.
Need to Calculate Mass Quickly?
Our Mass Calculator provides instant, accurate results for any object when you know its density and volume.
Mass vs. Weight: Understanding the Difference
Although mass and weight are often used interchangeably in everyday conversation, they represent different physical properties. This distinction is crucial for accurate scientific calculations and understanding physical phenomena.
Mass
- Measures the amount of matter in an object
- Remains constant regardless of location
- Measured in kilograms (kg), grams (g), etc.
- An intrinsic property of an object
- Not affected by gravitational field strength
Weight
- Measures the gravitational force acting on an object
- Changes based on location and gravitational field
- Measured in newtons (N), pounds (lb), etc.
- Depends on both mass and gravitational acceleration
- Formula: Weight = Mass × Gravitational Acceleration
For example, an astronaut with a mass of 70 kg would weigh approximately 686 N (154 lbs) on Earth but only about 114 N (26 lbs) on the Moon due to the Moon’s weaker gravitational field. However, the astronaut’s mass remains 70 kg in both locations.
Mass Measurement Units
Various units are used to measure mass across different fields and regions. Understanding these units and their conversions is essential for accurate calculations.
| Unit | Symbol | System | Equivalent in kg | Common Uses |
| Kilogram | kg | SI (metric) | 1 kg | Scientific measurements, everyday use in most countries |
| Gram | g | SI (metric) | 0.001 kg | Small measurements, food ingredients, laboratory work |
| Milligram | mg | SI (metric) | 0.000001 kg | Pharmaceuticals, chemistry, very small measurements |
| Pound | lb | Imperial/US | 0.45359237 kg | Common in US for body weight, food, general measurements |
| Ounce | oz | Imperial/US | 0.02834952 kg | Food measurements, small items in US and UK |
| Metric Ton | t | Metric | 1,000 kg | Shipping, large industrial measurements |
Convert Between Mass Units Easily
Our Mass Calculator handles all unit conversions automatically, saving you time and preventing calculation errors.
How to Calculate Mass
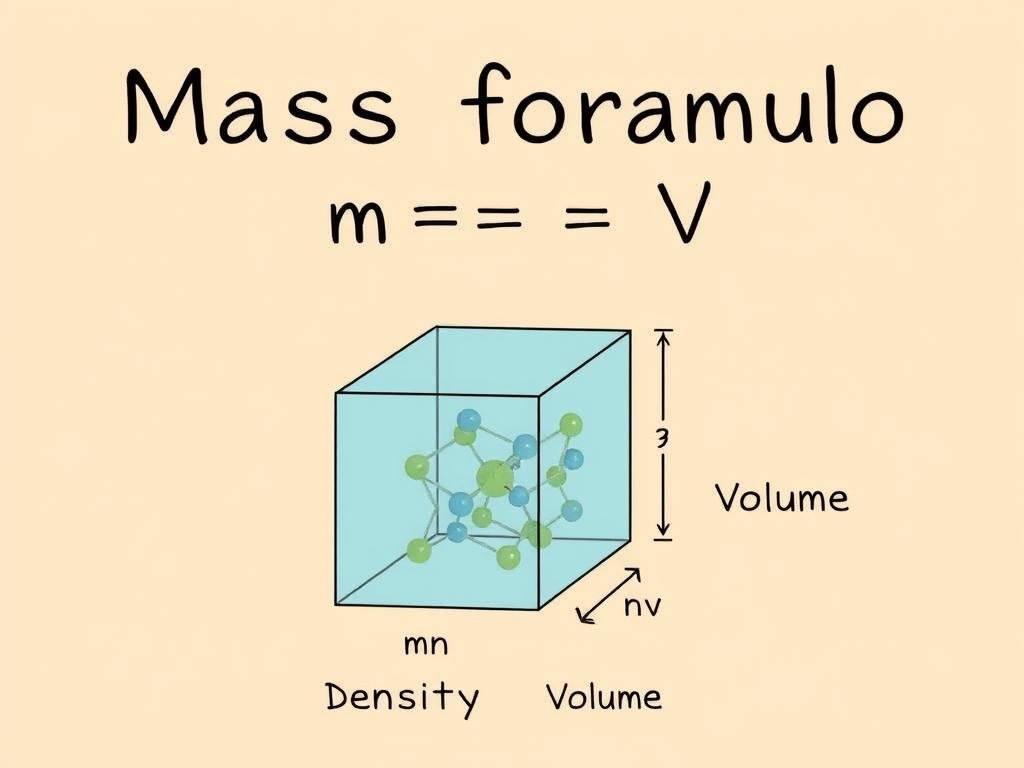
Mass Formula
The most common formula for calculating mass when density and volume are known is:
m = ρ × V
Where:
m = mass (kg)
ρ = density (kg/m³)
V = volume (m³)
This formula is derived from the definition of density, which is mass per unit volume. By rearranging the density formula (ρ = m/V), we can solve for mass.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
- Determine the density (ρ) of the material or substance in kg/m³
- Measure or calculate the volume (V) of the object in m³
- Multiply the density by the volume to find the mass
- Convert the result to the desired mass unit if necessary
Calculation Example
Problem: Calculate the mass of an aluminum block with a volume of 0.15 m³.
Given:
– Density of aluminum (ρ) = 2,700 kg/m³
– Volume (V) = 0.15 m³
Solution:
m = ρ × V
m = 2,700 kg/m³ × 0.15 m³
m = 405 kg
The aluminum block has a mass of 405 kilograms.
Practical Applications of Mass Calculations

Mass calculations are essential in numerous fields and everyday situations. Understanding how to calculate mass accurately can be valuable in various contexts:
Science & Research
- Laboratory experiments requiring precise measurements
- Chemical reactions and compound formulation
- Physics experiments and demonstrations
- Material science research and development
Engineering & Manufacturing
- Product design and material requirements
- Structural load calculations
- Quality control and material testing
- Transportation and shipping logistics
Everyday Applications
- Cooking and baking with precise measurements
- Shipping and postage calculations
- Fitness and nutrition tracking
- Home improvement and DIY projects
Calculate Mass for Any Application
Whether for professional work, education, or personal projects, our Mass Calculator provides accurate results for all your needs.
Alternative Mass Calculation Methods
While the density-volume method is common, there are several other ways to calculate mass depending on the available information:
| Formula | Variables | When to Use |
| m = F ÷ a | F = force, a = acceleration | When force and acceleration are known (Newton’s Second Law) |
| m = W ÷ g | W = weight, g = gravitational acceleration | When weight is measured and local gravity is known |
| m = E ÷ c² | E = energy, c = speed of light | In relativistic physics when dealing with energy-mass equivalence |
| m = n × M | n = number of moles, M = molar mass | In chemistry when dealing with substances in moles |
Each method has specific applications and limitations. The appropriate formula depends on the available data and the context of the calculation.
Benefits of Using an Online Mass Calculator

Time-Saving Benefits
- Instant calculations without manual computation
- Automatic unit conversions between different systems
- Ability to quickly recalculate with different parameters
- No need for reference tables or conversion charts
Accuracy Advantages
- Eliminates human calculation errors
- Precise to multiple decimal places when needed
- Consistent results every time
- Built-in validation to prevent impossible combinations
Experience These Benefits Yourself
Our Mass Calculator offers all these advantages and more, making your calculations faster, easier, and more accurate.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mass Calculations

What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location. Weight is the force of gravity acting on an object and varies depending on the gravitational field strength. On Earth, we often use weight to infer mass because the gravitational field is relatively constant across the surface.
How accurate are mass calculations using density and volume?
The accuracy of mass calculations using density and volume depends on the precision of your density and volume measurements. For homogeneous materials with well-established density values, calculations can be very accurate. However, for irregular objects or materials with variable density, some margin of error should be expected.
Can I calculate the mass of a liquid using this method?
Yes, the mass formula (m = ρ × V) works for liquids as well as solids. You’ll need to know the density of the liquid and its volume. For common liquids like water (density ≈ 1,000 kg/m³), the calculation is straightforward. For other liquids, you’ll need to reference their specific density values.
How do temperature and pressure affect mass calculations?
Temperature and pressure don’t affect an object’s mass directly, but they can change its density and volume, which in turn affects mass calculations. For gases especially, density varies significantly with temperature and pressure changes. For precise calculations, you should use density values that correspond to the specific temperature and pressure conditions of your situation.
What units should I use for mass calculations?
For consistency in calculations, it’s best to use SI units: kilograms (kg) for mass, cubic meters (m³) for volume, and kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) for density. However, our Mass Calculator can handle various unit combinations and will perform the necessary conversions automatically.
Start Calculating Mass Accurately Today

Understanding mass and how to calculate it is fundamental in many fields of science, engineering, and everyday applications. Our Mass Calculator provides a simple, accurate way to determine the mass of any object when you know its density and volume.
Whether you’re a student working on physics problems, a professional needing precise measurements, or simply curious about the physical properties of objects around you, our calculator offers the accuracy and convenience you need.
Ready to Calculate Mass?
Try our free, easy-to-use Mass Calculator now and get instant, accurate results for any material or object.