Number Sequence Calculator helps you identify sequences, find next terms, and detect patterns quickly. Easy, accurate tool for math and problem-solving.
Number Sequence Calculator
Number sequences are ordered arrangements of numbers that follow specific patterns. From the Fibonacci sequence in nature to arithmetic progressions in financial planning, these mathematical patterns help us understand and predict values. Our comprehensive guide explains how to identify, analyze, and calculate different types of number sequences, providing you with the knowledge to solve sequence problems effectively.
What is a Number Sequence?
A number sequence is an ordered list of numbers that follow a specific pattern or rule. Each number in the sequence is called a term, and the position of a term is denoted by its index. The pattern that governs a sequence can be expressed as a formula, which allows us to calculate any term in the sequence without having to list all preceding terms.
Number sequences appear throughout mathematics and have numerous real-world applications. They help us model growth patterns, analyze financial trends, understand natural phenomena, and solve complex problems in science and engineering.
The key to working with sequences is identifying the underlying pattern. Once you recognize the pattern, you can determine the formula for finding any term in the sequence and predict future values with accuracy.
Common Types of Number Sequences
There are several types of number sequences, each with its own pattern and formula. Understanding these common sequence types will help you identify patterns and calculate terms more effectively.
Arithmetic Sequence
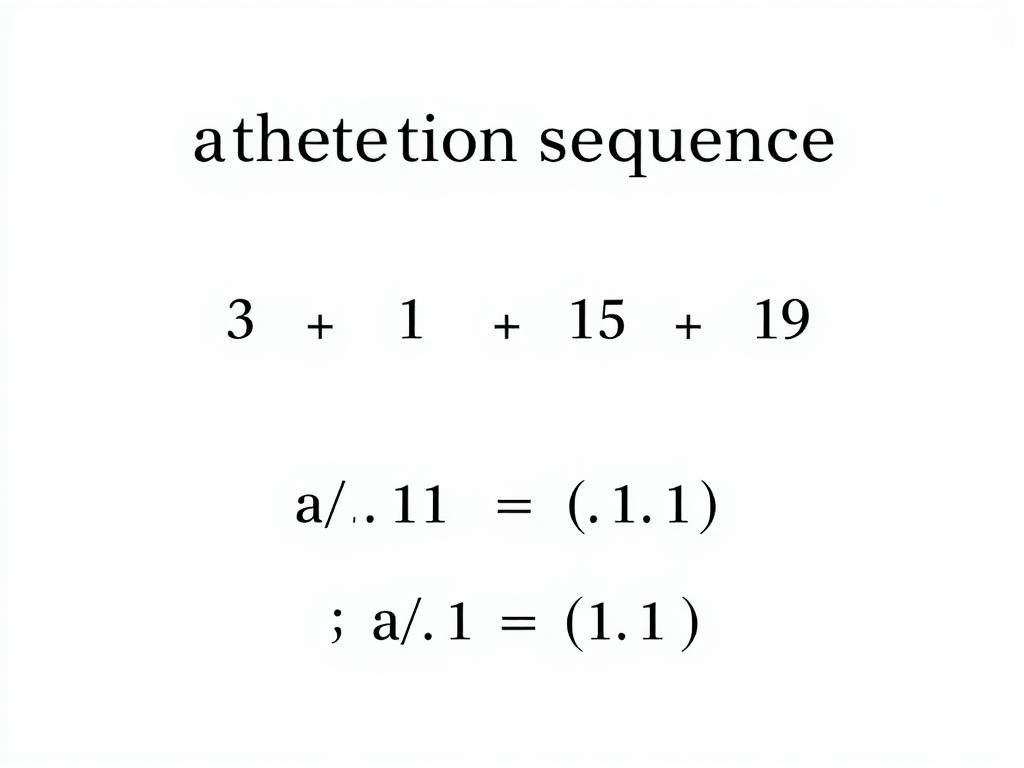
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. This constant difference is called the common difference.
Formula: an = a1 + (n-1) × d
Where:
- an is the nth term in the sequence
- a1 is the first term
- d is the common difference
- n is the position of the term
Example: In the sequence 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, …, the common difference is 4. Using the formula, we can find the 8th term:
a8 = 3 + (8-1) × 4 = 3 + 28 = 31
Geometric Sequence
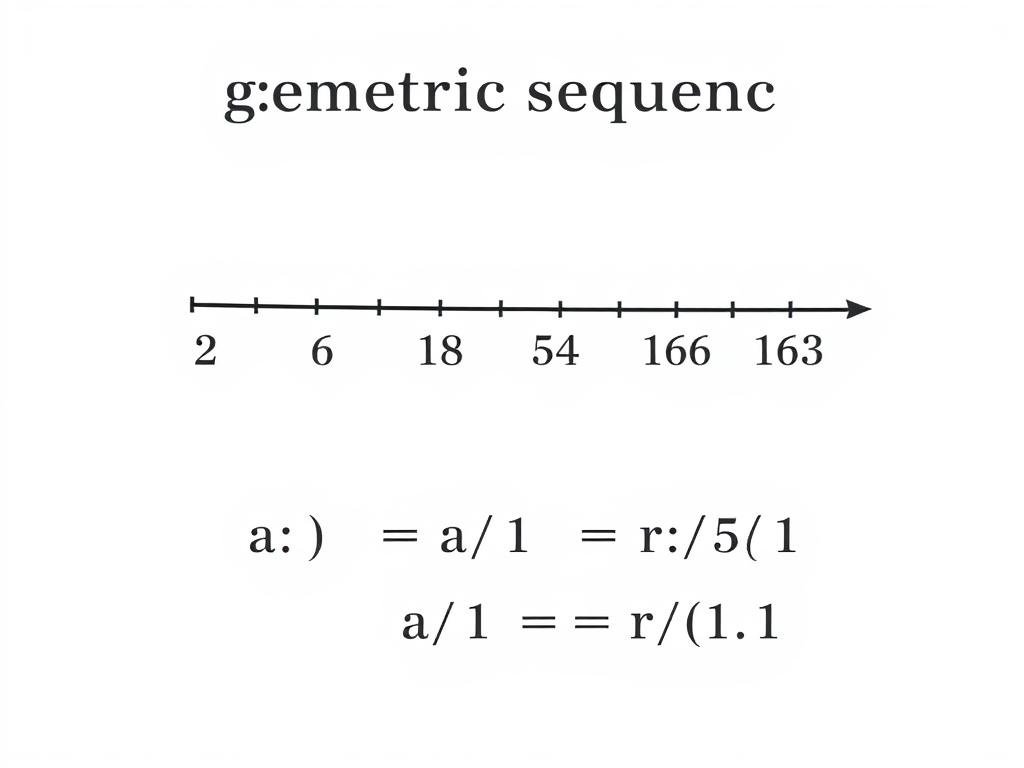
A geometric sequence is a list of numbers where each term is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio.
Formula: an = a1 × rn-1
Where:
- an is the nth term in the sequence
- a1 is the first term
- r is the common ratio
- n is the position of the term
Example: In the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, 162, …, the common ratio is 3. Using the formula, we can find the 6th term:
a6 = 2 × 36-1 = 2 × 35 = 2 × 243 = 486
Fibonacci Sequence
The Fibonacci sequence is a special sequence where each term is the sum of the two preceding terms. The sequence typically starts with 0 and 1.
Formula: Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
Where:
- Fn is the nth term in the sequence
- F0 = 0 and F1 = 1 (starting values)
Example: The first few terms of the Fibonacci sequence are 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, …
The Fibonacci sequence appears frequently in nature, such as in the arrangement of leaves on a stem, the spirals of shells, and the branching of trees.
Square Number Sequence
Square numbers are the result of multiplying a number by itself. The sequence of square numbers follows a specific pattern.
Formula: an = n2
Example: The sequence of square numbers is 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, …
Triangular Number Sequence
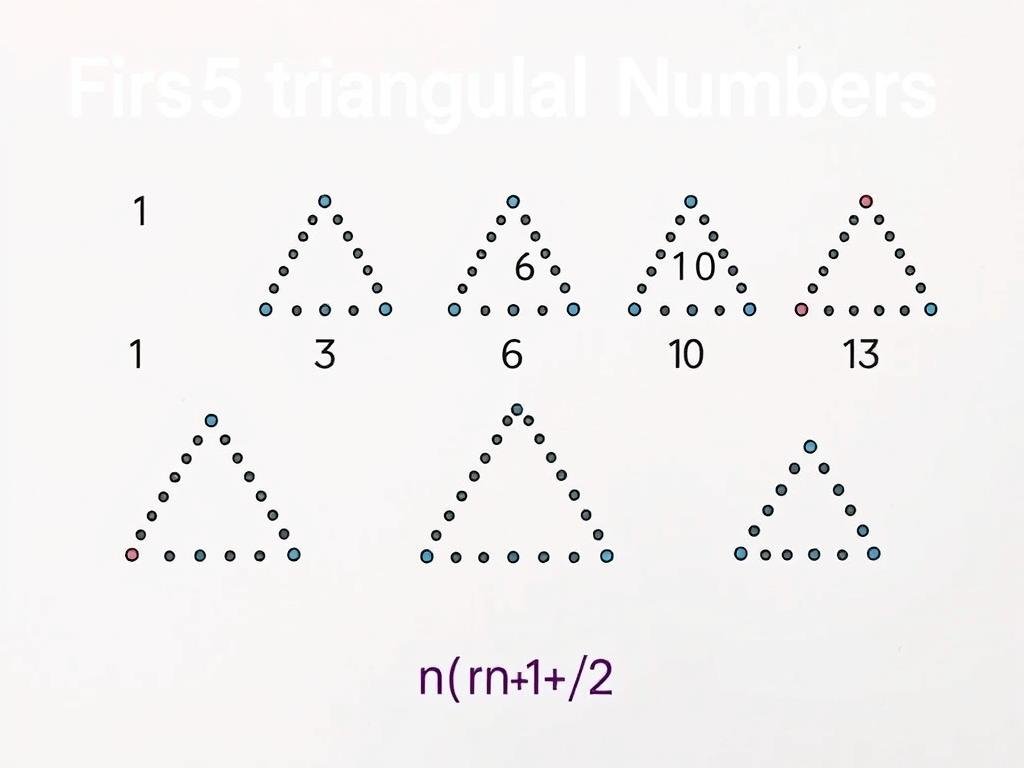
Triangular numbers represent the number of dots that can form an equilateral triangle. Each triangular number is the sum of the consecutive integers from 1 to n.
Formula: Tn = n(n+1)/2
Example: The sequence of triangular numbers is 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, …
How to Find the Next Number in a Sequence
Finding the next number in a sequence requires identifying the pattern that governs the sequence. Here’s a systematic approach to help you determine the next term:
Step 1: Look for Common Differences
Calculate the differences between consecutive terms. If these differences are constant, you’re dealing with an arithmetic sequence.
Example: For the sequence 5, 9, 13, 17, …
The differences are: 9-5=4, 13-9=4, 17-13=4
Since the difference is constant (4), this is an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 4. The next number would be 17+4=21.
Step 2: Check for Common Ratios
If the differences aren’t constant, check if each term can be obtained by multiplying the previous term by a constant value. If so, you have a geometric sequence.
Example: For the sequence 3, 6, 12, 24, …
The ratios are: 6÷3=2, 12÷6=2, 24÷12=2
Since the ratio is constant (2), this is a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 2. The next number would be 24×2=48.
Step 3: Test for Squared or Cubed Values
If neither of the above patterns works, check if the sequence consists of squared or cubed values, or other common mathematical operations.
Example: For the sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, …
These are 1², 2², 3², 4², so the next number would be 5²=25.
Step 4: Look for Alternating Patterns
Some sequences follow alternating patterns or combine multiple operations.
Example: For the sequence 2, 5, 10, 17, …
The differences are: 5-2=3, 10-5=5, 17-10=7
The differences between differences are: 5-3=2, 7-5=2
This suggests an arithmetic sequence of differences, making the original sequence quadratic. The next number would be 17+(7+2)=26.
How to Find the Formula of a Sequence
Determining the formula for a sequence allows you to calculate any term without listing all the previous terms. Here’s how to find the formula for different types of sequences:
For Arithmetic Sequences
To find the formula for an arithmetic sequence:
- Identify the first term (a1)
- Calculate the common difference (d) by subtracting any term from the term that follows it
- Apply the formula: an = a1 + (n-1) × d
Example: For the sequence 7, 10, 13, 16, …
First term a1 = 7
Common difference d = 10 – 7 = 3
Formula: an = 7 + (n-1) × 3 = 7 + 3n – 3 = 4 + 3n
For Geometric Sequences
To find the formula for a geometric sequence:
- Identify the first term (a1)
- Calculate the common ratio (r) by dividing any term by the term that precedes it
- Apply the formula: an = a1 × rn-1
Example: For the sequence 5, 15, 45, 135, …
First term a1 = 5
Common ratio r = 15 ÷ 5 = 3
Formula: an = 5 × 3n-1
For Quadratic Sequences
If the differences between consecutive terms form an arithmetic sequence, the original sequence is quadratic. The general form is:
an = an² + bn + c
To find the values of a, b, and c, you need to solve a system of equations using the first few terms of the sequence.
What is a Number Sequence Calculator?

A Number Sequence Calculator is a mathematical tool designed to help users work with various types of number sequences. These calculators can perform several functions related to sequences:
Key Functions
- Finding the nth term of a sequence
- Calculating the sum of a sequence
- Identifying the pattern or rule of a sequence
- Generating terms of a sequence
- Verifying if a number belongs to a sequence
Supported Sequence Types
- Arithmetic sequences
- Geometric sequences
- Fibonacci sequences
- Square and cubic sequences
- Triangular number sequences
- Custom sequences with user-defined rules
Number Sequence Calculators simplify complex calculations and help users understand the underlying patterns in sequences. They are valuable tools for students learning about sequences, teachers creating mathematical problems, and professionals working with mathematical models.
How to Use a Number Sequence Calculator
Using a Number Sequence Calculator effectively involves understanding the input parameters and interpreting the results correctly. Here’s a general guide on how to use such calculators:
Step 1: Identify Your Sequence Type
Before using the calculator, determine what type of sequence you’re working with. Is it arithmetic, geometric, Fibonacci, or another type? The sequence type will determine which parameters you need to input.
Step 2: Gather Required Information
Depending on the sequence type, you’ll need specific information:
- For arithmetic sequences: First term (a1) and common difference (d)
- For geometric sequences: First term (a1) and common ratio (r)
- For Fibonacci-like sequences: First two terms of the sequence
- For finding a specific term: The position (n) of the term you want to find
Step 3: Input Parameters
Enter the required parameters into the appropriate fields of the calculator. Make sure you’re using the correct units and format as specified by the calculator interface.
Step 4: Specify Your Calculation Goal
Indicate what you want to calculate:
- Finding a specific term (nth term)
- Calculating the sum of terms
- Generating a list of terms
- Finding the position of a specific value in the sequence
Step 5: Review and Interpret Results
After performing the calculation, review the results carefully. Most calculators will provide:
- The value of the requested term
- The sum of the sequence up to the specified term
- A list of terms in the sequence
- The formula used for the calculation
Understanding these results in the context of your original problem is crucial for applying the information correctly.
Benefits of Using a Number Sequence Calculator
- Time Efficiency: Quickly calculate terms and sums without manual computation
- Accuracy: Eliminate human calculation errors, especially with complex sequences
- Educational Value: Visualize patterns and relationships between terms
- Versatility: Handle multiple sequence types with a single tool
- Pattern Recognition: Help identify underlying rules in seemingly random number sets
- Accessibility: Make advanced mathematical concepts more approachable
- Problem-Solving: Tackle complex sequence problems with ease
Advantages of Number Sequence Calculators
Real-World Applications
Number Sequence Calculators have practical applications in various fields:
- Education: Teaching mathematical concepts and patterns
- Finance: Calculating compound interest and investment growth
- Computer Science: Algorithm development and data analysis
- Engineering: Modeling physical systems and predicting outcomes
- Architecture: Creating geometric patterns and proportional designs
- Biology: Analyzing growth patterns in populations
By leveraging the power of a Number Sequence Calculator, you can focus on understanding and applying the concepts rather than getting bogged down in tedious calculations.
Conclusion
Number sequences are fundamental mathematical concepts with wide-ranging applications in both theoretical and practical contexts. Understanding how to identify, analyze, and work with different types of sequences opens up new ways of perceiving patterns in the world around us.
A Number Sequence Calculator serves as a valuable tool for exploring these mathematical patterns, allowing you to quickly find specific terms, calculate sums, and verify your understanding of sequence rules. Whether you’re a student learning about sequences for the first time, a teacher creating educational materials, or a professional applying sequence concepts in your work, these calculators can significantly enhance your mathematical toolkit.
By mastering the concepts covered in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle sequence problems with confidence and gain deeper insights into the mathematical patterns that shape our world.
Ready to Explore Number Sequences?
Discover the patterns in your number sequences and solve complex mathematical problems with ease. Our Number Sequence Calculator helps you identify sequence types, find specific terms, and calculate sums accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a sequence and a series?
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers that follow a pattern, while a series is the sum of the terms in a sequence. For example, 2, 4, 6, 8, … is a sequence, and 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + … is the corresponding series.
How do I find the common difference in an arithmetic sequence?
To find the common difference in an arithmetic sequence, subtract any term from the term that follows it. For example, in the sequence 3, 7, 11, 15, the common difference is 7 – 3 = 4.
Can a Number Sequence Calculator find patterns in any set of numbers?
Most Number Sequence Calculators are designed to work with common sequence types like arithmetic, geometric, and Fibonacci sequences. While they can help identify patterns in many number sets, some complex or irregular patterns might require additional analysis or specialized tools.
How do I calculate the sum of an infinite geometric sequence?
For an infinite geometric sequence with first term a and common ratio r (where |r|
What are some real-life examples of the Fibonacci sequence?
The Fibonacci sequence appears in many natural phenomena, including the arrangement of leaves on plant stems (phyllotaxis), the spiral patterns of pinecones and sunflower seeds, the branching of trees, and the spiral shape of shells. It’s also found in the proportions of the human body and in various artistic compositions.