Use our Rent vs Buy Calculator to compare costs of renting and buying a home. Plan finances, evaluate options, and make informed housing decisions.
Deciding whether to rent or buy a home is one of the most significant financial choices you’ll make. Our Rent vs. Buy Calculator helps you cut through the complexity by analyzing your unique financial situation, local housing market conditions, and long-term goals. Stop guessing and start knowing which option truly makes the most financial sense for you.
Rent vs. Buy Calculator
Enter your details below to compare the financial impact of renting versus buying a home. Our calculator analyzes your unique situation to determine which option makes more sense for your budget and timeline.
How Our Rent vs. Buy Calculator Works
Our calculator takes the guesswork out of this major financial decision by analyzing both the short-term costs and long-term financial impact of renting versus buying. By entering specific details about your financial situation and housing options, you’ll get personalized insights that go beyond simple monthly payment comparisons.
Essential Calculator Inputs
Home Purchase Details
- Home price: The purchase price of the home you’re considering
- Down payment: The amount you plan to pay upfront (typically 3-20% of home price)
- Mortgage term: Length of your mortgage loan (typically 15 or 30 years)
- Interest rate: The annual interest rate on your mortgage
- Property tax rate: Annual property taxes as a percentage of home value
Rental Details
- Monthly rent: Your current or expected monthly rent payment
- Annual rent increase: Expected yearly percentage increase in rent
- Renter’s insurance: Monthly cost of insurance for renters
- Security deposit: One-time refundable deposit for rental property
Additional Financial Factors
Homeownership Costs
- Homeowner’s insurance: Annual cost to insure your home
- Maintenance costs: Estimated annual expenses for home upkeep (typically 1-2% of home value)
- HOA fees: Monthly homeowners association fees, if applicable
- Closing costs: One-time fees associated with finalizing your mortgage (typically 2-5% of loan amount)
- Home appreciation rate: Expected annual increase in your home’s value
Personal Financial Factors
- Length of stay: How long you plan to live in the home
- Investment return rate: Expected return if you invested money instead of buying
- Inflation rate: Expected annual increase in general prices
- Tax filing status: Your status for income tax purposes
- Marginal tax rate: Your tax bracket for income tax
Understanding Your Rent vs. Buy Calculator Results
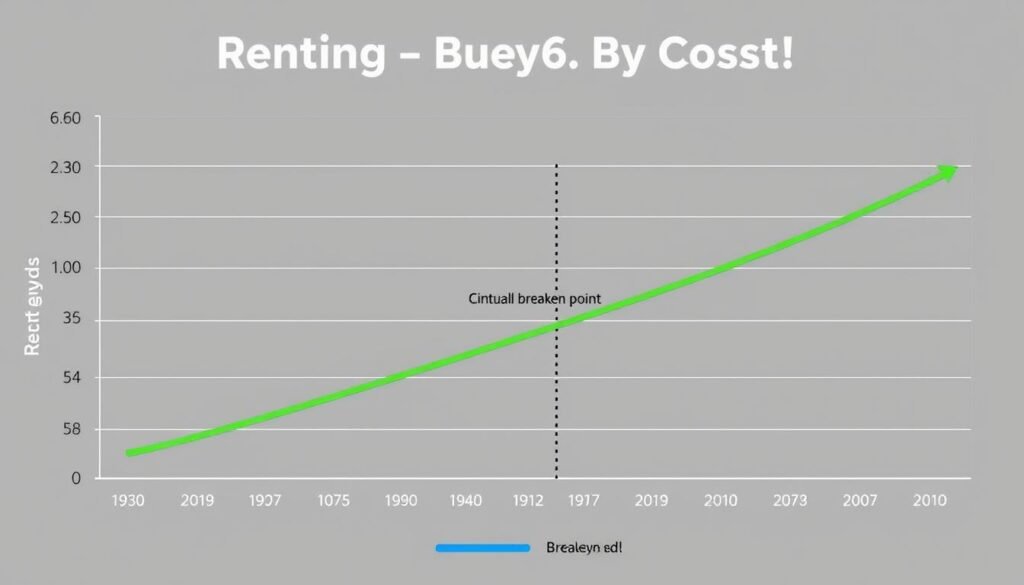
Sample comparison of cumulative costs over time with breakeven point highlighted
Key Metrics in Your Results
Monthly Cost Comparison
This shows your estimated monthly expenses for both renting and buying. For renting, this includes your rent payment and renter’s insurance. For buying, this includes your mortgage payment, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, and other recurring costs.
Breakeven Point
This crucial metric shows how many years you need to stay in the home before buying becomes more financially advantageous than renting. If you plan to move before this point, renting might be the better financial choice.
Long-Term Wealth Impact
This compares your total wealth under both scenarios after your planned stay. It factors in home equity, investment potential of savings, and the opportunity cost of your down payment.
When Buying Is Better Than Renting
Buying Advantages
- You plan to stay in the home longer than the breakeven point
- Home values in your area are appreciating at a healthy rate
- You benefit significantly from mortgage interest and property tax deductions
- You value building equity instead of “paying someone else’s mortgage”
- You desire the freedom to modify and personalize your living space
Buying Considerations
- Requires significant upfront costs (down payment, closing costs)
- You’re responsible for all maintenance and repair costs
- Less flexibility to relocate quickly for job opportunities
- Property values could decline, affecting your investment
- Additional costs like property taxes and insurance can increase over time

Homeownership offers stability and the pride of ownership beyond just financial considerations
When Renting Is Better Than Buying
Renting Advantages
- You plan to stay in the area for less time than the breakeven point
- You can invest the money you save on down payment and maintenance
- You value flexibility to relocate easily for career or lifestyle changes
- You prefer predictable monthly housing costs without surprise repairs
- Housing prices in your area are significantly overvalued
Renting Considerations
- Rent typically increases over time, sometimes unpredictably
- No equity building or ownership benefits
- Limited ability to customize or renovate your living space
- Potential restrictions on pets or lifestyle choices
- Less stability and security in your housing situation

Renting offers flexibility and freedom from maintenance responsibilities
Beyond the Numbers: Other Factors to Consider
Lifestyle Considerations
Personal Freedom
Homeownership gives you the freedom to renovate, decorate, and truly make a space your own. Want to paint the walls, install new fixtures, or remodel the kitchen? As a homeowner, these decisions are entirely yours. Renters typically face restrictions on modifications and must seek landlord approval for changes.
Mobility and Flexibility
Renting offers significantly more flexibility to relocate for job opportunities, lifestyle changes, or simply to experience different neighborhoods. Breaking a lease is generally easier and less costly than selling a home, which involves agent commissions, closing costs, and potential market timing issues.

Homeownership offers personalization while renting provides flexibility
Hidden Costs to Consider
| Expense Category | Homeowner Costs | Renter Costs |
| Upfront Costs | Down payment (3-20%), closing costs (2-5%), moving expenses | Security deposit (1-2 months rent), first/last month’s rent, moving expenses |
| Insurance | Homeowner’s insurance ($1,200-$2,500/year), possible PMI if down payment | Renter’s insurance ($150-$300/year) |
| Maintenance | 1-4% of home value annually for repairs, maintenance, and replacements | None (landlord responsible) |
| Utilities | All utilities (water, sewer, garbage, electricity, gas, etc.) | Some utilities (varies by rental agreement) |
| Property Taxes | 1-2% of home value annually (varies by location) | None (indirectly paid through rent) |
| Community Fees | HOA fees ($200-$600/month if applicable) | Amenity fees (if applicable) |
| Exit Costs | Agent commissions (5-6%), closing costs, potential capital gains tax | Potential lease break fee, cleaning fees |
Market Timing Considerations
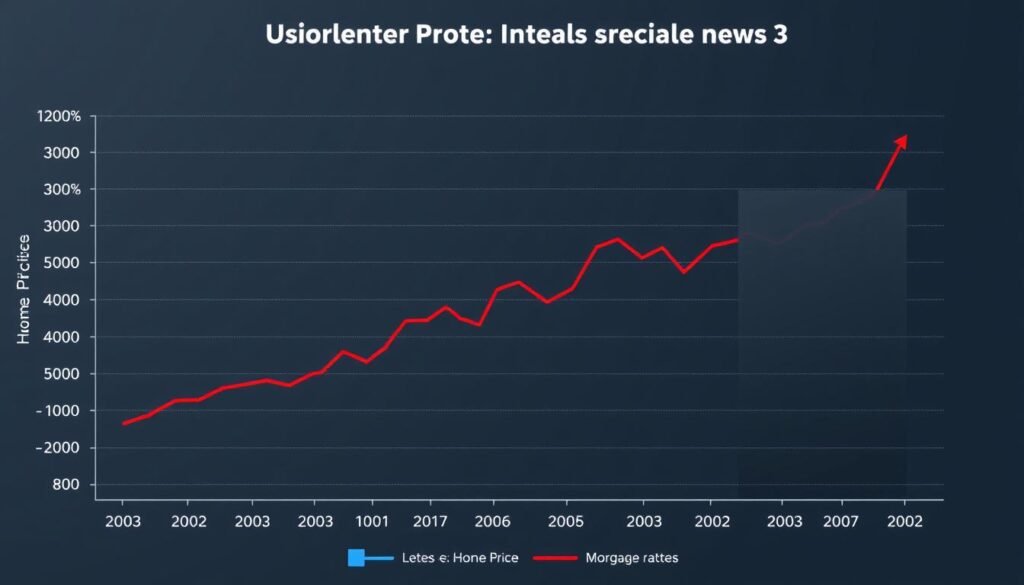
Historical home price trends and interest rate cycles impact the rent vs. buy equation
Interest Rate Environment
Mortgage interest rates significantly impact the cost of homeownership. When rates are low, monthly payments are lower and buying becomes more attractive. When rates are high, the same home becomes more expensive on a monthly basis, potentially tipping the scale toward renting.
Housing Market Conditions
Local market conditions matter tremendously. In a buyer’s market with declining prices, renting might be wiser until prices stabilize. In a seller’s market with rapidly appreciating values, buying sooner rather than later could be advantageous despite higher initial costs.
Tax Implications of Renting vs. Buying
Homeowner Tax Benefits
- Mortgage interest deduction: Interest paid on mortgages up to $750,000 is typically tax-deductible
- Property tax deduction: State and local property taxes can be deducted (subject to SALT limits)
- Capital gains exclusion: Up to $250,000 ($500,000 for married couples) in home sale profits may be tax-free
- Home office deduction: If you work from home, you may qualify for additional deductions
Renter Tax Considerations
- Standard deduction: Many renters benefit more from taking the standard deduction
- State-specific credits: Some states offer renter’s tax credits or rebates
- Investment deductions: If you invest the money saved by renting, you may qualify for investment-related tax benefits
- Simplicity: Typically fewer tax forms and calculations compared to homeowners
Tax Tip: The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act significantly increased the standard deduction while limiting itemized deductions, including mortgage interest and property taxes. This means fewer homeowners now benefit from itemizing these deductions. Always consult with a tax professional about your specific situation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Making Your Decision
-
Assess your financial readiness
Evaluate your savings, credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and job stability. Homeownership requires financial stability beyond just affording the monthly payment.
-
Determine your timeline
Honestly assess how long you plan to stay in one location. If it’s less than 3-5 years, renting often makes more financial sense due to the high transaction costs of buying and selling.
-
Research local market conditions
Investigate home prices, rental rates, and market trends in your target area. Some markets strongly favor buying while others favor renting.
-
Use our Rent vs. Buy Calculator
Enter your specific financial details and housing options to get a personalized analysis of which option makes more sense for your situation.
-
Consider non-financial factors
Weigh lifestyle preferences, desire for stability, maintenance responsibilities, and flexibility needs alongside the financial analysis.
-
Consult with professionals
Speak with a financial advisor, mortgage lender, and/or real estate professional to get expert insights tailored to your specific situation.
-
Make your decision with confidence
Armed with both financial analysis and consideration of personal factors, you can make a housing decision that aligns with both your financial goals and lifestyle needs.

Making an informed decision based on both calculator results and personal circumstances
Current Market Trends Affecting the Rent vs. Buy Decision
Interest Rate Environment
Mortgage rates have a significant impact on affordability. Higher rates increase monthly payments and may tip the scale toward renting in the short term. However, locking in a fixed-rate mortgage provides protection against future rate increases.
Housing Supply Constraints
Limited housing inventory in many markets has driven up both home prices and rental rates. In areas with severe supply constraints, buying may offer protection against rapidly rising rents despite higher initial costs.
Remote Work Flexibility
Increased remote work options have changed where people can live, opening up more affordable housing markets to buyers who previously needed to live in expensive urban centers for work.
Current market trends that influence the financial equation of renting vs. buying
Make Your Best Housing Decision Today
Stop wondering whether you should rent or buy. Our comprehensive Rent vs. Buy Calculator gives you personalized insights based on your unique financial situation and housing market. Make a confident, informed decision backed by data.

Whether renting or buying, making the right choice for your situation leads to satisfaction
Making Your Final Decision: Rent or Buy?
The rent versus buy decision is rarely just about numbers. While our calculator provides valuable financial insights, your final decision should incorporate both financial analysis and personal circumstances. Consider your lifestyle needs, career plans, desire for stability or flexibility, and comfort with maintenance responsibilities.
Remember that neither renting nor buying is inherently “better” – the right choice depends entirely on your unique situation. By using our Rent vs. Buy Calculator and considering the factors we’ve discussed, you can make a confident, informed decision that aligns with both your financial goals and personal preferences.
Take the first step toward housing clarity today by using our free Rent vs. Buy Calculator.
Ready to Make an Informed Housing Decision?
Our Rent vs. Buy Calculator gives you personalized insights based on your unique financial situation.