Use our Savings Calculator to estimate how your savings grow over time. Plan contributions, interest, and future balance to achieve your financial goals.
Planning for your financial future starts with understanding how your money can grow over time. Whether you’re saving for a home down payment, building an emergency fund, or preparing for retirement, knowing how your savings will accumulate is crucial to reaching your goals. Our savings calculator helps you visualize your financial journey and make informed decisions about your saving strategy.
With just a few simple inputs, you can map out your savings growth and adjust your plan to align with your financial objectives. Let’s explore how our calculator can help you take control of your financial future.
Savings Calculator
Use our calculator to see how your savings could grow over time. Enter your starting amount, monthly contribution, interest rate, and time period to get started.
Our user-friendly savings calculator helps you visualize your financial growth
How to Use This Savings Calculator
Our savings calculator is designed to be intuitive and easy to use, helping you map out your financial goals with just a few simple inputs. Here’s how to get the most out of this powerful tool:

Required Information
- Starting Amount: Enter your initial deposit or current savings balance. This is the principal amount that will begin earning interest immediately.
- Monthly Contribution: Specify how much you plan to add to your savings each month. Consistent contributions significantly impact your long-term growth.
- Annual Interest Rate (APY): Input the annual percentage yield your account earns. This can vary widely between different savings vehicles like traditional savings accounts, high-yield savings accounts, or CDs.
- Time Period: Select how many years or months you plan to save. Longer time frames allow compound interest to work more effectively.
- Compound Frequency: Choose how often interest is calculated and added to your account (daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually).
Understanding Your Results
After entering your information, the calculator will display several key results:
- Final Balance: The total amount you’ll have at the end of your selected time period.
- Total Contributions: The sum of your initial deposit and all monthly contributions.
- Interest Earned: The amount generated through compound interest over time.
Ready to see your savings potential?
Try different scenarios to find the saving strategy that works best for your financial goals.
Understanding Savings Growth
The growth of your savings depends on several key factors that work together to build your wealth over time. Understanding these elements will help you make more informed decisions about your saving strategy.
The Power of Compound Interest
Compound interest is often called the eighth wonder of the world for good reason. Unlike simple interest, which is calculated only on your principal amount, compound interest is calculated on both the principal and the accumulated interest. This creates a snowball effect that accelerates your savings growth over time.
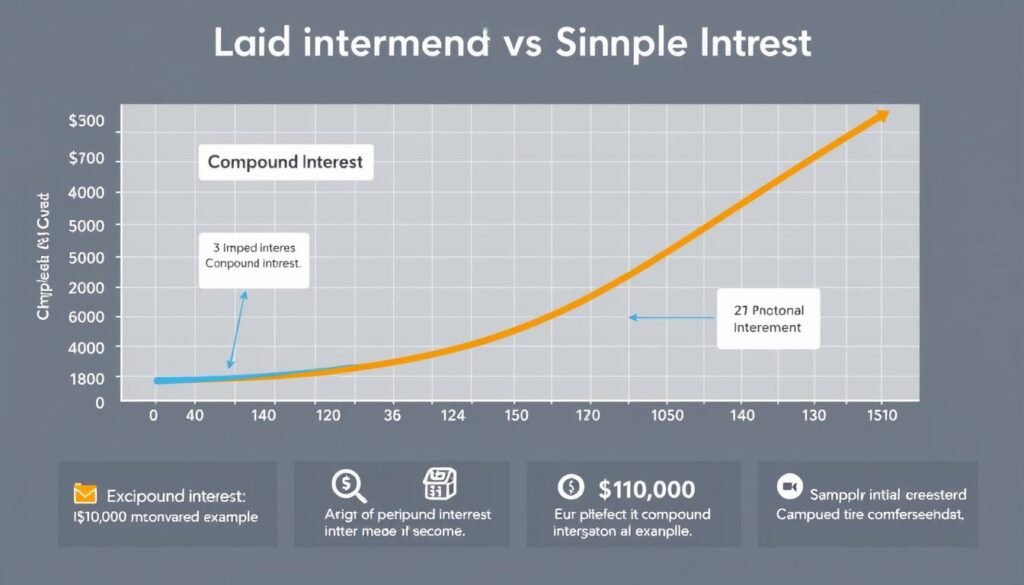
Compound interest creates exponential growth compared to simple interest
“Compound interest is the most powerful force in the universe. He who understands it, earns it; he who doesn’t, pays it.”
Time: Your Most Valuable Asset
When it comes to savings, time is truly your most powerful ally. The longer your money has to grow, the more dramatic the effects of compounding become. Starting early, even with smaller amounts, often leads to better results than waiting and investing larger sums later.
Consider this example: If you start saving $200 monthly at age 25 with a 5% annual return, by age 65 you’ll have approximately $304,000. Wait until age 35 to start the same savings plan, and you’ll have only about $165,000 by age 65 – a difference of $139,000 despite only contributing $24,000 less.
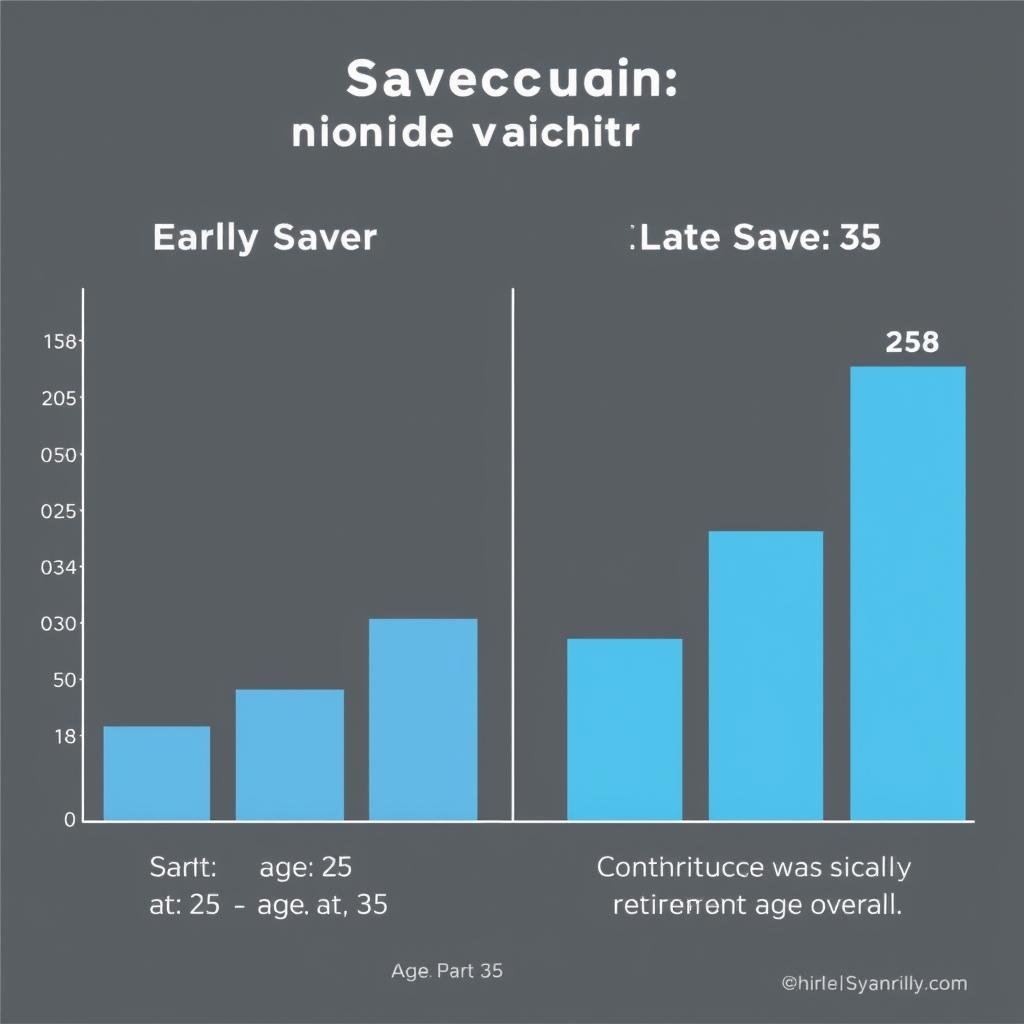
Consistency Matters
Regular contributions to your savings account can dramatically impact your long-term results. Even modest monthly deposits add up significantly over time and benefit from compound interest. Our calculator allows you to see how consistent saving habits can transform your financial future.
Pro Tip: Try running the calculator with and without monthly contributions to see the dramatic difference that regular deposits make to your final balance.
Types of Savings Accounts
Different savings vehicles offer varying benefits in terms of interest rates, accessibility, and features. Understanding these options helps you choose the right account for your specific financial goals.
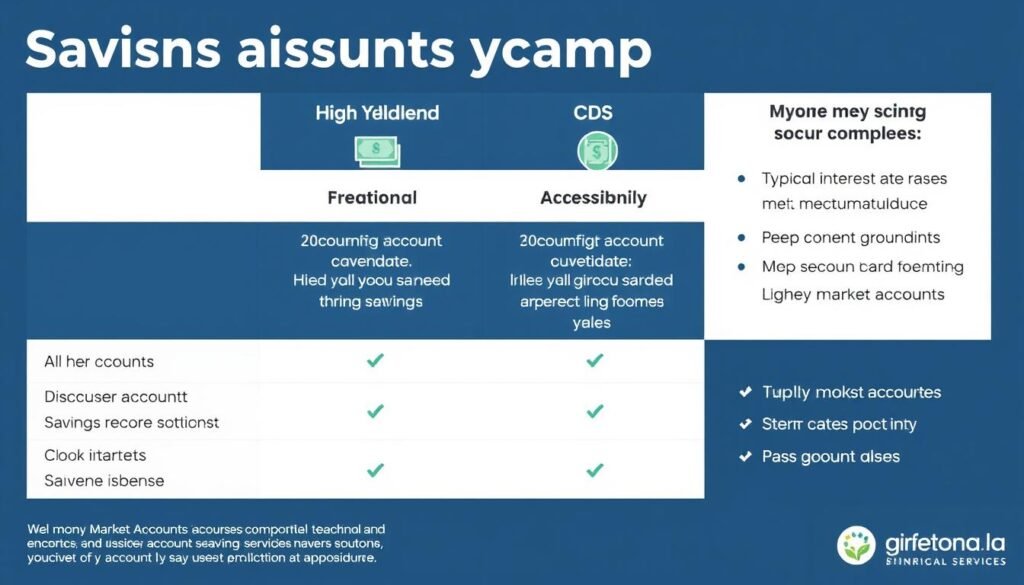
| Account Type | Typical APY Range | Liquidity | Minimum Balance | Best For |
| Traditional Savings | 0.01% – 0.1% | High | $0 – $25 | Everyday savings, quick access |
| High-Yield Savings | 0.5% – 5.0% | Medium-High | $0 – $100 | Emergency funds, short-term goals |
| Certificates of Deposit (CDs) | 0.5% – 5.5% | Low (term-based) | $500 – $1,000 | Known future expenses, higher returns |
| Money Market Accounts | 0.3% – 4.0% | Medium | $1,000 – $2,500 | Balance between access and returns |
Traditional Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts offered by brick-and-mortar banks typically provide easy access to your money but offer lower interest rates. These accounts are FDIC-insured and suitable for funds you might need to access quickly, such as emergency savings.
High-Yield Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts generally offer interest rates significantly higher than traditional savings accounts. Often provided by online banks with lower overhead costs, these accounts maintain liquidity while maximizing your interest earnings.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
CDs offer fixed interest rates for a specified term length, typically ranging from three months to five years. While they often provide higher rates than savings accounts, they restrict access to your funds until maturity without incurring penalties.
Money Market Accounts
Money market accounts combine features of checking and savings accounts, sometimes offering check-writing privileges while providing higher interest rates than traditional savings. They typically require higher minimum balances but offer more flexibility than CDs.
Compare Your Options
Use our calculator to compare how your money would grow in different account types with varying interest rates.
Effective Savings Strategies
Developing a solid savings strategy helps you maximize growth and reach your financial goals more efficiently. Here are some proven approaches to consider:

Set Clear Savings Goals
Having specific, measurable savings goals gives your financial plan direction and purpose. Whether you’re saving for a home down payment, emergency fund, or retirement, defining clear targets helps you track progress and stay motivated.
Automate Your Savings
Setting up automatic transfers from your checking to savings account ensures consistency and removes the temptation to spend before saving. Many financial experts recommend the “pay yourself first” approach, where savings are automatically deducted before you have a chance to spend.
Automation Tip: Schedule automatic transfers to coincide with your payday to ensure saving happens before spending.
Follow the 50/30/20 Rule
This popular budgeting approach suggests allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment. This balanced framework helps ensure you’re saving adequately while still meeting your current needs.
Build a CD Ladder
A CD ladder involves dividing your savings among multiple CDs with different maturity dates. This strategy provides regular access to portions of your savings while still benefiting from the higher rates that longer-term CDs typically offer.
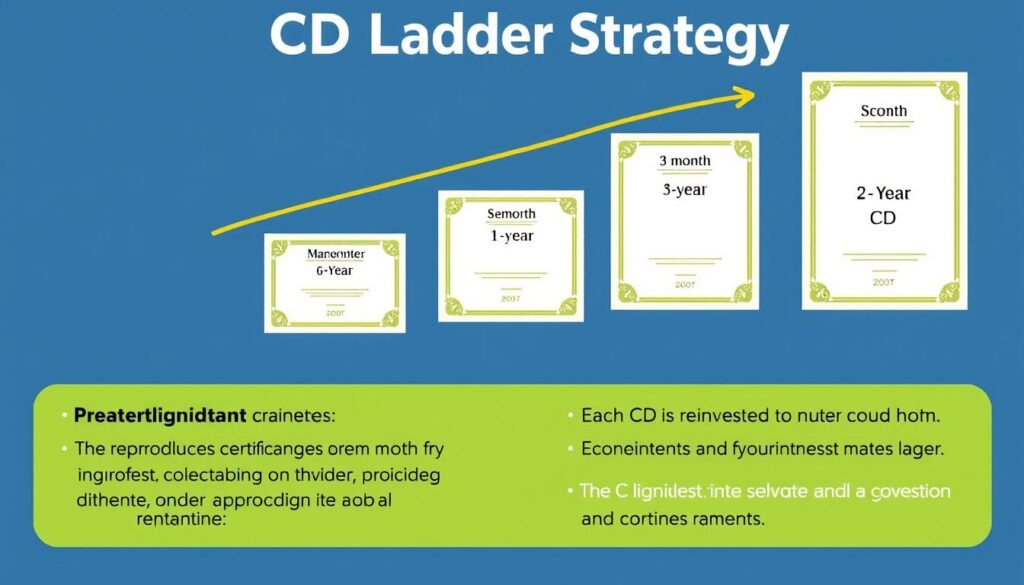
A CD ladder provides regular access to funds while maximizing interest rates
Diversify Your Savings
Spreading your savings across different account types can help you balance liquidity needs with growth potential. Consider keeping emergency funds in high-yield savings accounts for easy access, while longer-term savings might be better suited for CDs or investment accounts.
Calculate Your Savings Strategy
Use our calculator to test different savings strategies and find the approach that best fits your financial goals.
The Math Behind Savings Calculations
Understanding the formulas used in savings calculations can help you better appreciate how your money grows over time. Our calculator handles these complex equations automatically, but knowing the underlying math gives you deeper insight into your financial planning.
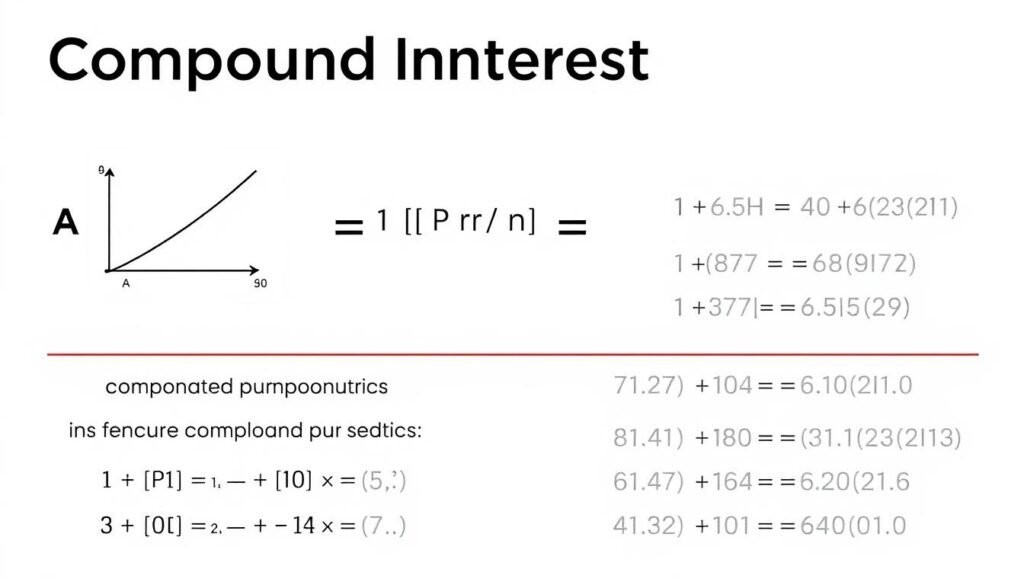
Compound Interest Formula
The basic formula for compound interest is:
A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt)
Where:
- A = Final amount
- P = Principal (initial investment)
- r = Annual interest rate (decimal)
- n = Number of times interest compounds per year
- t = Time in years
Regular Contributions Formula
When you make regular contributions to your savings, the formula becomes more complex:
A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) + PMT × ((1 + r/n)^(nt) – 1) / (r/n)
Where PMT represents your regular contribution amount.
Example Calculation
Let’s walk through a simple example:
Initial deposit: $1,000
Monthly contribution: $100
Annual interest rate: 5% (0.05)
Compounding: Monthly (12 times per year)
Time period: 5 years
Using the formula:
A = $1,000(1 + 0.05/12)^(12×5) + $100 × ((1 + 0.05/12)^(12×5) – 1) / (0.05/12)
A = $1,000 × 1.28 + $100 × 65.7
A = $1,280 + $6,570 = $7,850
After 5 years, you would have approximately $7,850, with $1,000 from your initial deposit, $6,000 from monthly contributions, and $850 in interest.
Skip the Math: Our savings calculator handles all these complex calculations instantly, allowing you to focus on planning your financial future.
Real-World Savings Scenarios
To help illustrate how our savings calculator can assist with various financial goals, let’s explore some common real-world scenarios.
Building an Emergency Fund
Financial experts recommend having 3-6 months of essential expenses saved in an emergency fund. For someone with $3,000 in monthly expenses, that means a target of $9,000-$18,000.
Scenario: Starting with $1,000 and contributing $400 monthly to a high-yield savings account earning 4% APY.
Result: You would reach $10,000 in approximately 22 months, with about $9,000 from contributions and $1,000 from interest.
Saving for a Home Down Payment
With median home prices in many areas exceeding $300,000, a 20% down payment means saving $60,000 or more.
Scenario: Starting with $10,000 and contributing $750 monthly to a combination of high-yield savings and short-term CDs averaging 3.5% APY.
Result: You would reach $60,000 in approximately 5 years, with about $55,000 from deposits and $5,000 from interest.
College Fund for a Child
With college costs rising annually, starting early is crucial for parents saving for their children’s education.
Scenario: Starting when your child is born with $2,000 and contributing $200 monthly to a 529 plan earning an average of 6% annually.
Result: By your child’s 18th birthday, you would have approximately $83,000, with about $45,000 from contributions and $38,000 from investment growth.
Calculate Your Personal Scenario
Enter your specific savings goal and timeline to see how you can achieve your financial objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much should I save each month?
The ideal monthly savings amount varies based on your income, expenses, and financial goals. Many financial experts recommend saving at least 20% of your income using the 50/30/20 rule (50% for needs, 30% for wants, 20% for savings). However, any consistent amount you can save is beneficial. Use our savings calculator to experiment with different monthly contribution amounts to see how they impact your long-term savings growth.
What is compound interest and why is it important?
Compound interest is interest earned on both your principal balance and previously accumulated interest. It’s important because it creates exponential growth over time, significantly increasing your savings without additional contributions. The more frequently interest compounds (daily, monthly, quarterly), the faster your money grows. This is why starting to save early is so powerful – it gives compound interest more time to work in your favor.
How do I choose the best savings account?
When selecting a savings account, consider these key factors:
- Interest rate (APY) – higher rates mean faster growth
- Compounding frequency – more frequent compounding accelerates growth
- Minimum balance requirements – ensure you can meet these to avoid fees
- Access to funds – consider how quickly you might need the money
- Fees – look for accounts with minimal or no monthly maintenance fees
- FDIC/NCUA insurance – ensure your deposits are protected
High-yield savings accounts from online banks often offer the best combination of competitive rates and low fees.
How often should I recalculate my savings plan?
It’s wise to review your savings plan at least annually or whenever you experience significant life changes such as:
- Income changes (raises, job changes, additional income sources)
- Major expense changes (housing, family size)
- Interest rate fluctuations in the broader economy
- Changes to your financial goals or timelines
Regular recalculation helps ensure you stay on track to meet your goals and allows you to adjust your strategy as needed.
Is a savings account the best place for all my money?
While savings accounts are excellent for emergency funds and short-term goals, they may not be optimal for all your financial objectives. For long-term goals like retirement, investment accounts typically offer higher returns despite greater short-term volatility. A balanced financial strategy often includes:
- Savings accounts for emergency funds and short-term goals (0-3 years)
- CDs for medium-term goals (1-5 years)
- Investment accounts for long-term goals (5+ years)
Consider consulting with a financial advisor to create a comprehensive plan tailored to your specific situation.
Ready to start growing your savings?
Use our calculator to create a personalized savings plan that helps you reach your financial goals.
Take Control of Your Financial Future
Understanding how your savings can grow over time is a powerful step toward achieving financial security and reaching your goals. Our savings calculator provides the insights you need to make informed decisions about your saving strategy, helping you visualize the impact of different variables on your financial future.
Remember that successful saving is about consistency, patience, and making informed choices. By regularly contributing to your savings, choosing the right account types for your goals, and giving your money time to grow through compound interest, you can build a solid financial foundation for whatever life brings.
Start using our savings calculator today to map out your path to financial success. Your future self will thank you for the steps you take now to secure your financial well-being.
Begin Your Savings Journey
Take the first step toward your financial goals with our easy-to-use calculator.