Convert numbers to scientific notation or calculate with them instantly. Our Scientific Notation Calculator makes math quick, accurate, and hassle-free.
Scientific Notation Calculator
Scientific notation makes working with very large or small numbers manageable. Whether you’re a student learning this mathematical concept, a scientist recording precise measurements, or an engineer performing complex calculations, our Scientific Notation Calculator simplifies the process of converting between standard and scientific notation.
Ready to Convert Numbers?
Our calculator handles both conversion and mathematical operations with scientific notation.
What is Scientific Notation?
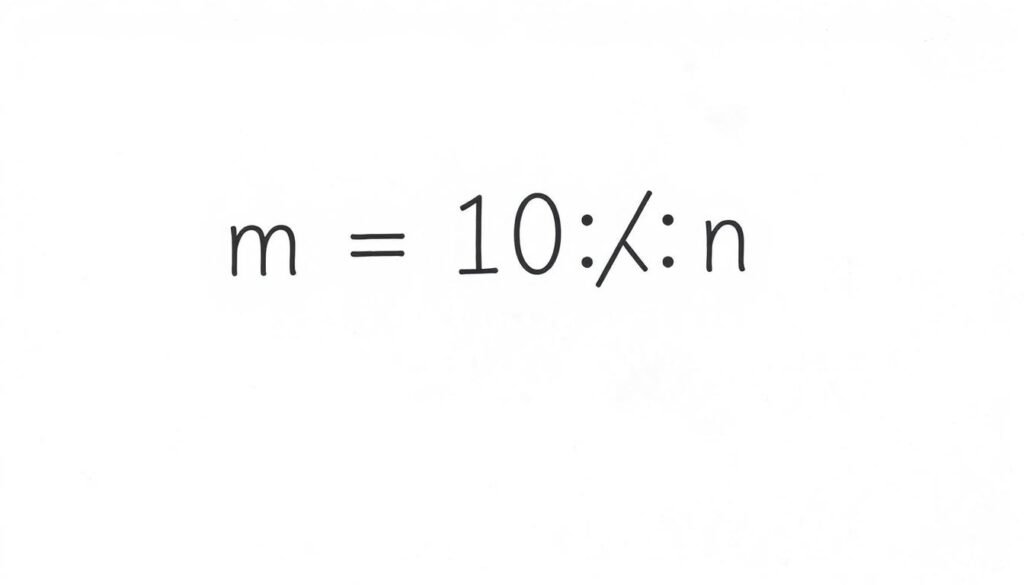
Scientific notation expresses numbers as a coefficient multiplied by a power of 10
Scientific notation is a standardized way to write very large or very small numbers in a more concise and readable format. In scientific notation, a number is expressed as a coefficient (between 1 and 10) multiplied by a power of 10.
The standard format is:
m × 10n
Where:
- m is the coefficient (or significand) – a number between 1 and 10
- n is the exponent – an integer that indicates how many places to move the decimal point
This notation is particularly useful in scientific fields where researchers work with extremely large numbers (like astronomical distances) or extremely small numbers (like atomic measurements).
Need to convert a number to scientific notation?
Examples of Scientific Notation
| Standard Form | Scientific Notation | E-Notation |
| 5,000 | 5 × 103 | 5e+3 |
| 1,000,000 | 1 × 106 | 1e+6 |
| 0.0004212 | 4.212 × 10-4 | 4.212e-4 |
| -5,000,000,000 | -5 × 109 | -5e+9 |
| 0.000000000000123 | 1.23 × 10-13 | 1.23e-13 |

How to Convert to Scientific Notation

Converting a number to scientific notation involves following these simple steps:
- Move the decimal point in the original number until there is exactly one non-zero digit to the left of the decimal point.
- Count how many places you moved the decimal point.
- If you moved the decimal point to the left, the exponent is positive. If you moved it to the right, the exponent is negative.
- Write the number in the form m × 10n, where m is the number with the adjusted decimal point and n is the exponent.
Example: Converting 45,600 to Scientific Notation
Step 1: Move the decimal point until there is exactly one non-zero digit to the left.
45,600 → 4.5600
Step 2: Count how many places you moved the decimal point.
The decimal point was moved 4 places to the left.
Step 3: Determine the sign of the exponent.
Since the decimal point was moved to the left, the exponent is positive: +4
Step 4: Write in scientific notation.
45,600 = 4.56 × 104
Convert your numbers to scientific notation instantly!
How to Convert from Scientific Notation to Standard Form
Converting from scientific notation back to standard form is just as straightforward:
- Identify the coefficient (m) and the exponent (n) in the scientific notation m × 10n.
- If the exponent is positive, move the decimal point in the coefficient to the right by n places.
- If the exponent is negative, move the decimal point in the coefficient to the left by n places.
- Add zeros as needed when moving the decimal point.
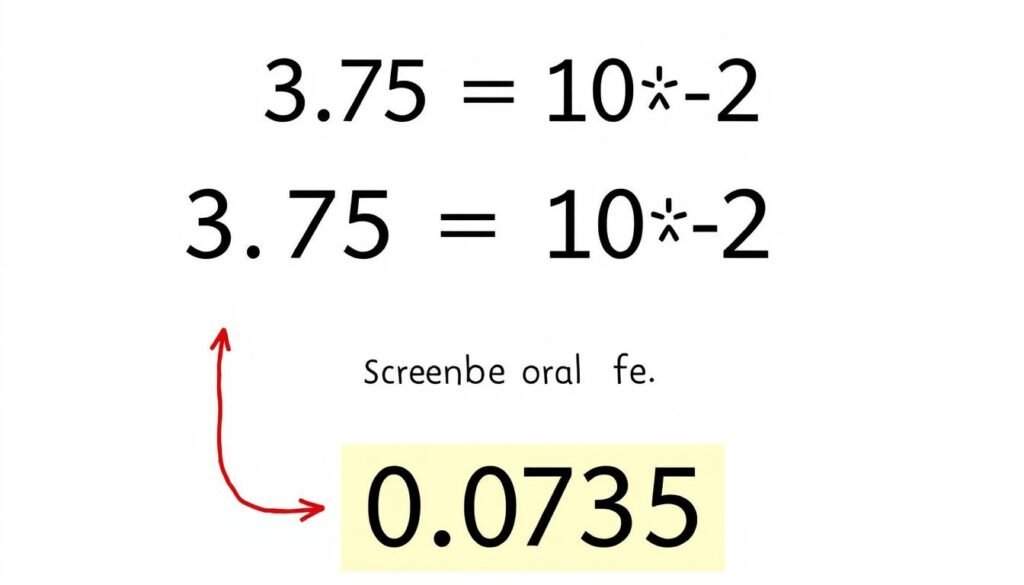
Example: Converting 3.75 × 10-2 to Standard Form
Step 1: Identify the coefficient and exponent.
Coefficient (m) = 3.75
Exponent (n) = -2
Step 2: Since the exponent is negative, move the decimal point to the left by 2 places.
3.75 → 0.0375
Step 3: The standard form is 0.0375
Need to convert from scientific notation to standard form?
Understanding E-Notation
E-notation is a variation of scientific notation commonly used in calculators and computer programming. Instead of using “× 10n“, E-notation uses “E” or “e” followed by the exponent.
For example:
- 5 × 103 in scientific notation is written as 5E3 or 5e3 in E-notation
- 4.212 × 10-4 is written as 4.212E-4 or 4.212e-4
E-notation is particularly useful in programming and when working with calculators that have limited display capabilities. Our Scientific Notation Calculator supports both traditional scientific notation and E-notation formats.
Engineering Notation: A Practical Variant
Engineering notation is a variation of scientific notation where the exponent is always a multiple of 3 (e.g., 103, 106, 10-3, 10-6). This makes it align perfectly with SI prefixes like kilo (103), mega (106), milli (10-3), etc.
For example:
- 4.5 × 106 (scientific notation) = 4.5 × 106 (engineering notation) = 4.5 megaunits
- 1.23 × 105 (scientific notation) = 123 × 103 (engineering notation) = 123 kilounits
Engineers prefer this notation because it makes it easier to read measurements with standard metric prefixes. Our Scientific Notation Calculator can convert numbers to engineering notation as well.
Performing Calculations with Scientific Notation
One of the main advantages of scientific notation is that it simplifies arithmetic operations with very large or small numbers. Here’s how to perform basic calculations:
Multiplication
To multiply numbers in scientific notation:
- Multiply the coefficients
- Add the exponents
- Convert the result to proper scientific notation if needed
Example: (2.5 × 104) × (3.0 × 10-2)
= (2.5 × 3.0) × (104 × 10-2)
= 7.5 × 104+(-2)
= 7.5 × 102
Division
To divide numbers in scientific notation:
- Divide the coefficients
- Subtract the exponent of the denominator from the exponent of the numerator
- Convert the result to proper scientific notation if needed
Example: (8.4 × 105) ÷ (2.1 × 103)
= (8.4 ÷ 2.1) × (105 ÷ 103)
= 4.0 × 105-3
= 4.0 × 102
Addition and Subtraction
For addition and subtraction, the exponents must be the same:
- Convert all numbers to the same power of 10
- Add or subtract the coefficients
- Keep the same exponent
- Convert the result to proper scientific notation if needed
Example: (3.0 × 105) + (4.5 × 104)
First, convert to the same exponent: (3.0 × 105) + (0.45 × 105)
= (3.0 + 0.45) × 105
= 3.45 × 105
Let our calculator handle complex scientific notation operations for you!
Real-World Applications of Scientific Notation

Astronomy
Astronomers use scientific notation to express cosmic distances:
- Distance to the Moon: 3.84 × 108 meters
- Distance to the Sun: 1.496 × 1011 meters
- Distance to the nearest star (Proxima Centauri): 4.0 × 1016 meters
Microbiology
Microbiologists use scientific notation for tiny measurements:
- Size of a typical bacterium: 1 × 10-6 meters
- Size of a virus: 1 × 10-8 meters
- Size of a DNA molecule width: 2.5 × 10-9 meters
Computing
Computer scientists use scientific notation for data sizes:
- 1 Gigabyte: 1 × 109 bytes
- 1 Terabyte: 1 × 1012 bytes
- Global internet traffic per day: ~2.5 × 1018 bytes
Scientific notation is essential in fields where measurements can be extremely large or small. It allows scientists, engineers, and mathematicians to work with these numbers efficiently and avoid errors that might occur when writing out all the zeros.
Benefits of Using a Scientific Notation Calculator

Advantages of Using Our Calculator
- Eliminates manual conversion errors
- Saves time on complex calculations
- Handles both conversion and arithmetic operations
- Supports multiple notation formats (scientific, engineering, E-notation)
- Perfect for students learning the concept
- Ideal for professionals who need quick, accurate results
Challenges Without a Calculator
- Manual conversions are prone to errors
- Complex calculations become time-consuming
- Difficult to verify results without a reference
- Steep learning curve for beginners
- Easy to miscount decimal places
- Hard to perform operations with mixed notations
Experience These Benefits Yourself!
Our Scientific Notation Calculator makes working with extreme numbers simple and error-free.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between scientific notation and E-notation?
Scientific notation expresses numbers in the form m × 10n, while E-notation replaces “× 10n” with “E” or “e” followed by the exponent. For example, 3.5 × 106 in scientific notation is written as 3.5E6 or 3.5e6 in E-notation. Both represent the same value but use different formats.
When should I use scientific notation?
Scientific notation is most useful when working with very large numbers (like astronomical distances) or very small numbers (like atomic measurements). It’s also helpful when performing calculations with numbers of vastly different magnitudes or when you need to clearly express the precision of a measurement.
How do I convert negative numbers to scientific notation?
The process is the same as for positive numbers, but you keep the negative sign. For example, to convert -45,600 to scientific notation, you would get -4.56 × 104. The negative sign applies to the coefficient, not the exponent.
What’s the difference between scientific and engineering notation?
In scientific notation, the coefficient is always between 1 and 10. In engineering notation, the exponent is always a multiple of 3 (e.g., 103, 106, 10-3), which aligns with SI prefixes like kilo, mega, milli, etc. This means the coefficient in engineering notation can be between 1 and 999.9.
Master Scientific Notation with Our Calculator

Scientific notation is an essential mathematical tool that simplifies working with extremely large or small numbers. Whether you’re a student learning this concept for the first time, a scientist recording precise measurements, or an engineer performing complex calculations, our Scientific Notation Calculator makes the process simple and error-free.
With the ability to convert between different notation formats and perform arithmetic operations, our calculator is the perfect companion for anyone working with scientific notation. Try it today and experience the convenience of quick, accurate conversions and calculations!
Ready to Simplify Your Calculations?
Our Scientific Notation Calculator handles conversions and operations with extreme numbers effortlessly.