Use our 401K Calculator to estimate your retirement savings growth. Plan contributions, employer matches, and future balance to secure your financial future.
Planning for retirement can feel overwhelming, but understanding how your 401(k) contributions grow over time is a crucial step toward financial security. Our 401K Calculator helps you visualize your retirement savings journey, factoring in employer matches, contribution rates, and investment returns. Whether you’re just starting your career or nearing retirement, this tool provides the clarity you need to make informed decisions about your financial future.
401K Calculator Tool
Use our interactive calculator to estimate your 401(k) balance at retirement based on your current savings, contribution rate, and employer match.
Our 401K Calculator helps you visualize your retirement savings growth over time
What Is a 401(k) Plan?
A 401(k) is a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan offered by employers that allows employees to save and invest a portion of their paycheck before taxes are taken out. These plans are named after subsection 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code, which was established by the Revenue Act of 1978.
How 401(k) Plans Work
When you contribute to a 401(k), the money is automatically deducted from your paycheck and invested in funds of your choosing from options provided by your employer’s plan. These contributions reduce your taxable income for the year, potentially lowering your tax bill. The funds in your 401(k) grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw the money in retirement.
Types of 401(k) Plans
Traditional 401(k)
Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your current taxable income. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
Roth 401(k)
Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, so you pay taxes upfront. Qualified withdrawals in retirement are completely tax-free, including earnings.
Benefits of Using a 401K Calculator
Advantages of 401(k) Plans
- Tax-advantaged growth allows your investments to compound more efficiently
- Employer matching contributions provide “free money” toward your retirement
- Higher contribution limits compared to IRAs ($23,500 for 2025, $31,000 for those over 50)
- Automatic payroll deductions make saving consistent and effortless
- Creditor protection shields your retirement assets in case of bankruptcy
Limitations of 401(k) Plans
- Limited investment options compared to IRAs or brokerage accounts
- Early withdrawal penalties (10%) if you access funds before age 59½
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) starting at age 73
- Potential vesting periods for employer contributions
- Administrative fees may be higher than other retirement accounts
Using our 401K Calculator helps you understand how these benefits and limitations affect your specific retirement situation, allowing you to make more informed decisions about your contributions and investment strategy.
How to Use Our 401K Calculator
Follow these steps to get an accurate projection of your retirement savings
Ready to Calculate Your Retirement Savings?
Use our calculator to see how your 401(k) contributions can grow over time.
401(k) Contribution Limits
The IRS sets annual limits on how much you can contribute to your 401(k) plan. Understanding these limits helps you maximize your retirement savings strategy.
| Age Group | 2025 Contribution Limit | Catch-Up Contribution | Total Possible Contribution |
| Under 50 | $23,500 | $0 | $23,500 |
| 50-59 | $23,500 | $7,500 | $31,000 |
| 60-63 | $23,500 | $11,250 | $34,750 |
Note: The combined limit for both employee and employer contributions for 2025 is $70,000 or 100% of employee compensation, whichever is less.
Pro Tip: If you’re over 50, take advantage of catch-up contributions to boost your retirement savings. Our 401K Calculator can help you see the impact of these additional contributions on your retirement balance.
Understanding Employer Match
One of the most valuable features of a 401(k) plan is the employer match. This is essentially free money that your employer contributes to your retirement account based on your own contributions.
Common employer matching formulas and their impact on your retirement savings
Common Matching Formulas
- Employer contributes $1 for every $1 you contribute
- Match applies up to a certain percentage of your salary
- Example: 100% match up to 3% means if you contribute 3% of your salary, your employer adds another 3%
- Total contribution: 6% of your salary
100% Match up to X%
- Employer contributes $0.50 for every $1 you contribute
- Match applies up to a certain percentage of your salary
- Example: 50% match up to 6% means if you contribute 6%, your employer adds 3%
- Total contribution: 9% of your salary
50% Match up to X%
- Different match rates for different contribution levels
- Example: 100% on first 3%, then 50% on next 2%
- If you contribute 5%, employer adds 4% (3% + 1%)
- Total contribution: 9% of your salary
Tiered Match
Always contribute enough to get your full employer match! Not taking advantage of your employer’s matching contribution is like leaving free money on the table. Use our 401K Calculator to see how employer matching affects your retirement savings over time.
Vesting Schedules and Your 401(k)
While your personal contributions to your 401(k) are always 100% vested (meaning they’re completely yours), employer contributions often come with vesting schedules. Vesting determines how much of your employer’s contributions you get to keep if you leave the company.
Types of Vesting Schedules
Cliff Vesting
With cliff vesting, you must work for your employer for a specific period (typically 3 years) before you’re entitled to any of the employer-contributed money. Once you reach that cliff, you become 100% vested all at once.
Graded Vesting
Graded vesting gives you ownership of your employer’s contributions gradually over time. For example, you might be 20% vested after 2 years, 40% after 3 years, and so on until you’re fully vested.
Immediate Vesting
Some employers offer immediate vesting, meaning you own 100% of their contributions as soon as they’re made to your account.
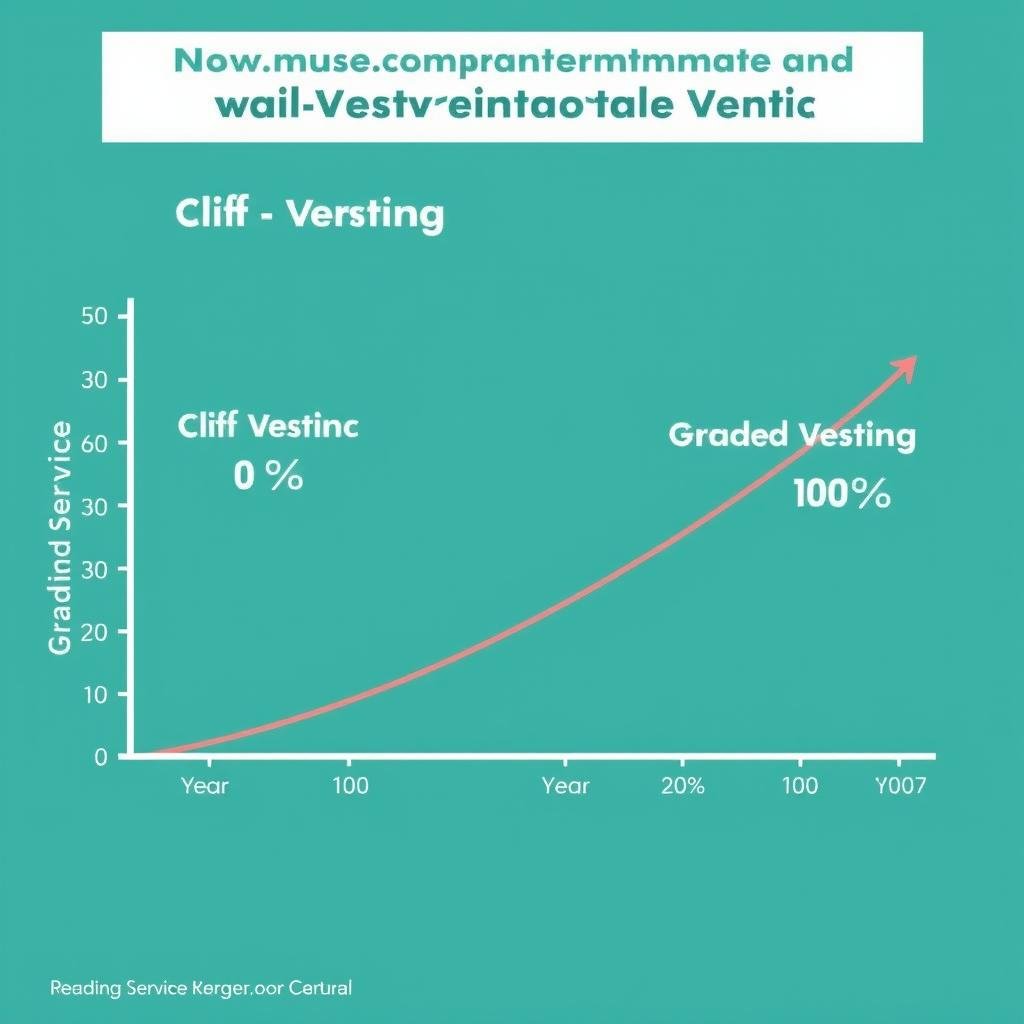
Comparison of cliff vesting vs. graded vesting schedules over a 5-year period
Important: When changing jobs, consider your vesting status. Leaving before you’re fully vested means forfeiting some employer contributions. Our 401K Calculator can help you factor in vesting schedules when planning job changes.
Early Withdrawal Considerations
While 401(k) plans are designed for long-term retirement savings, there may be circumstances where you need to access your funds before retirement age. Understanding the implications of early withdrawals is crucial for making informed decisions.
Warning: Early withdrawals from your 401(k) before age 59½ typically incur a 10% penalty in addition to regular income taxes, potentially reducing your withdrawal amount by 30% or more.
Penalty Exceptions for Early Withdrawals
Hardship Withdrawals
- Medical expenses exceeding 7.5% of adjusted gross income
- Costs related to purchasing a principal residence
- Tuition and educational fees for the next 12 months
- Payments to prevent eviction or foreclosure
- Funeral or burial expenses
- Expenses for repairing damage to principal residence
Non-Hardship Exceptions
- Permanent disability
- Medical expenses that qualify for tax deduction
- Court-ordered payments to a divorced spouse, child, or dependent
- Separation from service after age 55
- Substantially equal periodic payments (SEPP) under Rule 72(t)
The long-term impact of early withdrawals on retirement savings
Calculate the True Cost of Early Withdrawals
Use our 401K Early Withdrawal Calculator to see how much a withdrawal would cost you in penalties and lost growth.
401(k) Loans: An Alternative to Withdrawals
If you need access to your 401(k) funds before retirement, taking a loan from your account may be a better option than an early withdrawal. Unlike withdrawals, loans allow you to borrow from yourself and repay the money with interest.
401(k) Loan Rules
- You can borrow up to 50% of your vested account balance or $50,000, whichever is less
- Loans typically must be repaid within 5 years (longer terms may be available for home purchases)
- Payments are made through payroll deductions with interest
- Interest you pay goes back into your account
- No taxes or penalties if loan terms are met
The 401(k) loan process from application to repayment
While a 401(k) loan avoids immediate taxes and penalties, it’s important to consider the opportunity cost of removing money from your retirement investments, even temporarily. The funds you borrow won’t be growing tax-deferred during the loan period.
Risks of 401(k) Loans
Job Change Risk: If you leave your job (voluntarily or involuntarily), your loan typically becomes due within 60-90 days. If you can’t repay it, the outstanding balance is treated as a distribution, subject to taxes and possibly the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Use our 401K Loan Calculator to understand how a loan might affect your retirement savings and to compare it with other borrowing options.
401(k) Investment Options
Most 401(k) plans offer a variety of investment options to help you grow your retirement savings. Understanding these options is crucial for building a portfolio that aligns with your risk tolerance and retirement timeline.
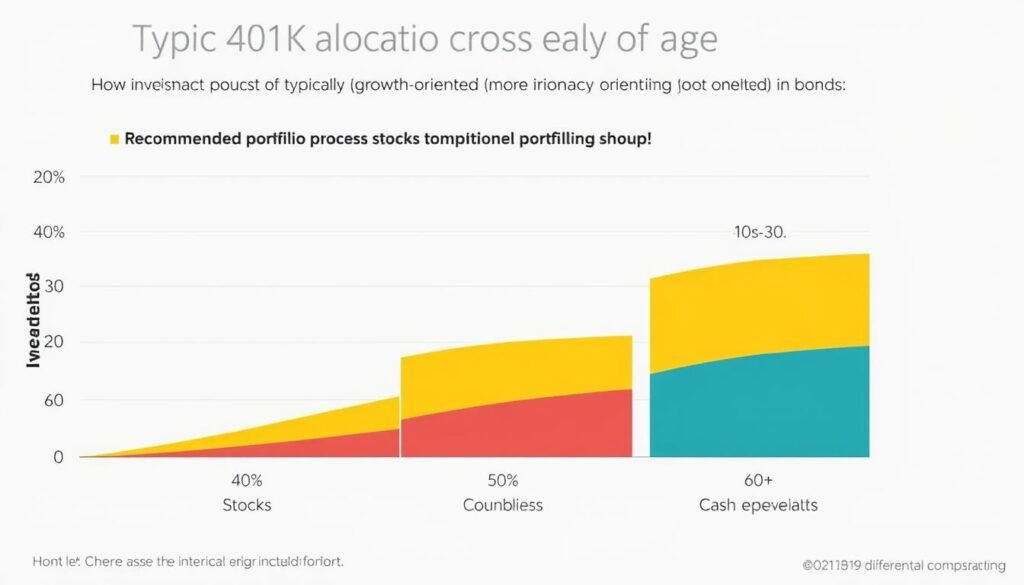
Typical asset allocation strategies by age group for 401(k) investors
Common Investment Options
Target-Date Funds
These “set it and forget it” funds automatically adjust your asset allocation based on your expected retirement date, becoming more conservative as you approach retirement.
Best for: Investors who prefer a hands-off approach
Index Funds
These funds track specific market indexes like the S&P 500, offering broad market exposure with low fees and minimal management.
Best for: Cost-conscious investors seeking market returns
Actively Managed Funds
Professional fund managers select investments with the goal of outperforming the market, typically with higher fees than index funds.
Best for: Investors willing to pay for potential outperformance
Bond Funds
These funds invest in corporate or government bonds, providing income and typically less volatility than stock funds.
Best for: Conservative investors or those nearing retirement
Stable Value Funds
These conservative investments aim to preserve capital while providing steady, modest returns above money market rates.
Best for: Very conservative investors or short-term goals
Company Stock
Some plans offer the option to invest in your employer’s stock, which can be risky due to lack of diversification.
Best for: Limited portion of portfolio if you believe in company growth
Investment Strategy Tip: Consider the “Rule of 100” for basic asset allocation. Subtract your age from 100 to get the approximate percentage of your portfolio to allocate to stocks. For example, if you’re 40, consider allocating about 60% to stocks and 40% to bonds and cash equivalents.
Use our Asset Allocation Calculator to determine an appropriate investment mix based on your age, risk tolerance, and retirement goals.
401(k) Rollovers When Changing Jobs
When you change jobs, you have several options for your existing 401(k) account. Understanding these options helps you make the best decision for your retirement savings.
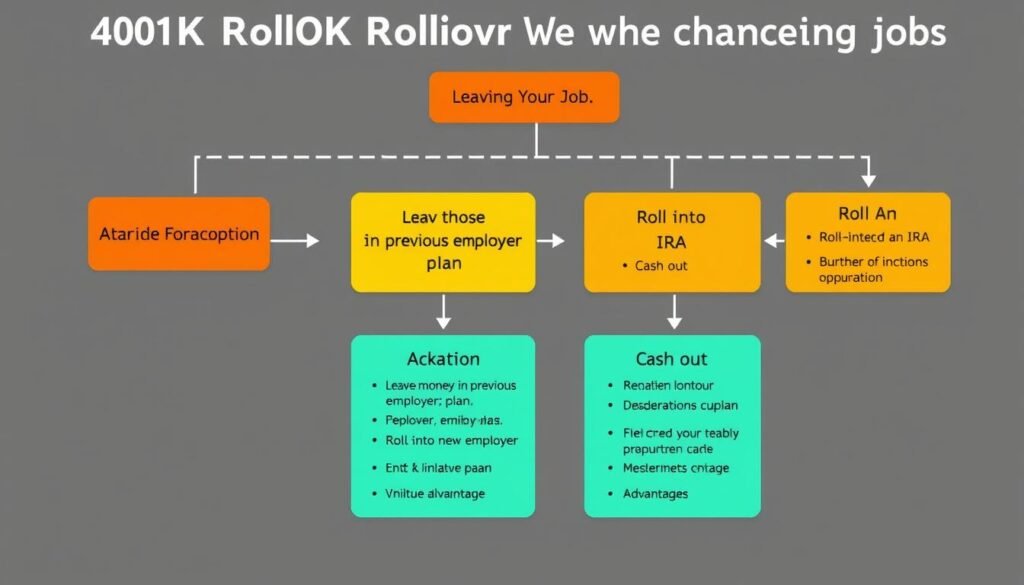
Decision flowchart for 401(k) options when changing employers
Your Options When Changing Jobs
- Consolidates retirement accounts
- Continues tax-deferred growth
- May offer better investment options
- Maintains creditor protection
- Potential for loans (if plan allows)
Roll Into New Employer’s Plan
- More investment options
- Continues tax-deferred growth
- No employer restrictions
- Easier to manage with one account
- Potential for lower fees
Roll Into an IRA
- No immediate action needed
- Familiar investment options
- Maintains tax-deferred status
- Some plans have good, low-cost options
- Separation of retirement assets
Leave in Previous Employer’s Plan
Avoid Cashing Out: Taking a distribution from your 401(k) when changing jobs results in taxes and potential penalties. Additionally, you lose the power of tax-deferred growth on those funds. For most people, this should be a last resort.
Direct vs. Indirect Rollovers
Direct Rollover (Recommended)
In a direct rollover, funds move directly from your old plan to your new plan or IRA without passing through your hands. This avoids tax withholding and simplifies the process.
Indirect Rollover (60-Day Rollover)
With an indirect rollover, you receive a check for your distribution minus 20% tax withholding. You must deposit the full amount (including the withheld portion) into a new retirement account within 60 days to avoid taxes and penalties.
Compare Your Rollover Options
Use our 401(k) Rollover Calculator to see how different rollover strategies might affect your retirement savings.
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Once you reach age 73 (or age 72 if you reached that age before December 31, 2022), the IRS requires you to start taking distributions from your traditional 401(k) accounts. These are called Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs).
RMD factors by age – showing how the required withdrawal percentage increases over time
RMD Rules and Calculations
- First RMD deadline: April 1 of the year following the year you turn 73
- Subsequent RMDs: By December 31 of each year
- Calculation method: Account balance as of December 31 of the previous year divided by your life expectancy factor (from IRS tables)
- Penalty for missing RMDs: 25% excise tax on the amount not taken (reduced to 10% if corrected in a timely manner)
- Exception: If you’re still working for the company that sponsors your 401(k) and don’t own more than 5% of the company, you may be able to delay RMDs from that plan until you retire
Roth 401(k) Note: Unlike Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k) accounts are subject to RMDs. However, you can roll your Roth 401(k) into a Roth IRA to avoid RMDs.
Use our RMD Calculator to estimate your required distributions based on your age and account balance.
Tax Considerations for Your 401(k)
Understanding the tax implications of your 401(k) contributions, growth, and withdrawals is essential for effective retirement planning.
Traditional 401(k) Tax Treatment
- Contributions: Made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your current taxable income
- Growth: Tax-deferred – no taxes on dividends, interest, or capital gains while in the account
- Withdrawals: Taxed as ordinary income when distributed in retirement
- Early withdrawals: Subject to income tax plus 10% penalty if taken before age 59½ (with some exceptions)
Roth 401(k) Tax Treatment
- Contributions: Made with after-tax dollars, no current tax deduction
- Growth: Tax-free – no taxes on dividends, interest, or capital gains
- Qualified withdrawals: Completely tax-free if account is at least 5 years old and you’re at least 59½
- Early withdrawals: Contributions can be withdrawn tax-free, but earnings may be subject to tax and penalty
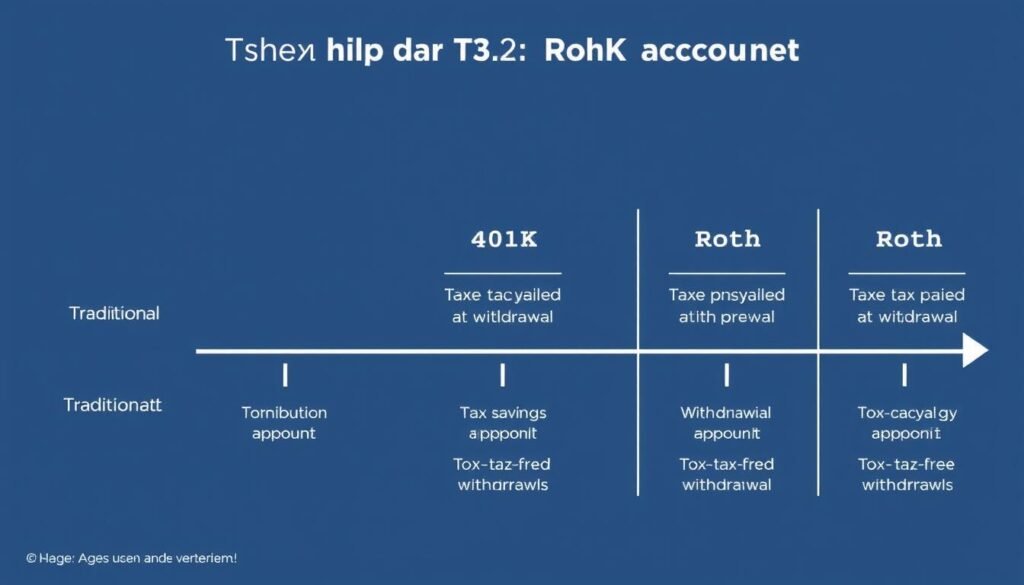
Tax treatment comparison: Traditional vs. Roth 401(k) over your lifetime
Which Is Better: Traditional or Roth 401(k)?
The traditional vs. Roth decision often comes down to whether you expect to be in a higher or lower tax bracket in retirement than you are now. If you expect to be in a higher bracket later, Roth contributions may be more advantageous. If you expect to be in a lower bracket, traditional contributions might be better.
Compare Traditional vs. Roth 401(k)
Use our calculator to see which type of 401(k) might be better for your specific situation.
Strategies for Maximizing Your 401(k)
Implementing these strategies can help you get the most out of your 401(k) plan and build a more secure retirement.
Start Early
The power of compound growth means that even small contributions made early in your career can grow significantly over time. Starting in your 20s instead of your 30s can potentially add hundreds of thousands of dollars to your retirement balance.
Capture Full Employer Match
At minimum, contribute enough to get your full employer match. This is essentially free money that provides an immediate return on your investment regardless of market performance.
Increase Contributions Gradually
Consider increasing your contribution percentage each time you get a raise. Since you’re already accustomed to living without that money, you won’t feel the pinch of the increased retirement savings.
Diversify Investments
Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk. Review and rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Minimize Fees
Pay attention to investment fees, which can significantly impact your returns over time. Low-cost index funds often provide better long-term results than actively managed funds with higher fees.
Use Catch-Up Contributions
If you’re 50 or older, take advantage of catch-up contributions to boost your savings in the years leading up to retirement. The additional $7,500 per year can significantly increase your retirement balance.
The impact of different maximization strategies on a $100,000 starting balance over 30 years
Calculate Your Optimal Contribution Strategy
Use our 401K Maximizer Calculator to find the contribution strategy that works best for your retirement goals.
Start Planning Your Retirement Today
Your 401(k) is one of the most powerful tools available for building retirement security. By understanding how these plans work and using our calculators to make informed decisions, you can take control of your financial future and work toward a comfortable retirement.
Remember that retirement planning is a journey, not a one-time event. Regularly reviewing your contributions, investment allocations, and retirement goals will help you stay on track as your life circumstances change.
Ready to Calculate Your 401(k) Future?
Use our comprehensive suite of retirement calculators to plan your path to financial security.
For more retirement planning resources, check out our Retirement Planning Guides or explore our full suite of financial calculators.
Frequently Asked Questions About 401(k) Plans
What happens to my 401(k) if I change jobs?
When you change jobs, you typically have four options for your existing 401(k):
- Roll it over to your new employer’s 401(k) plan
- Roll it over to an Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
- Leave it with your former employer’s plan (if allowed)
- Cash it out (not recommended due to taxes and penalties)
Most financial advisors recommend option 1 or 2 to maintain the tax-advantaged status of your retirement savings and keep your money growing for retirement.
How much should I contribute to my 401(k)?
Financial experts typically recommend contributing at least enough to get your full employer match. Beyond that, aim to save 10-15% of your income for retirement (including employer contributions). If possible, maxing out your annual contribution limit provides the greatest tax advantage and retirement security.
Use our 401K Calculator to determine how different contribution rates might affect your retirement balance.
Can I lose money in my 401(k)?
Yes, 401(k) investments are subject to market risk, and their value can fluctuate based on market performance. However, historical data shows that over long periods, diversified portfolios tend to grow despite short-term market volatility. The risk of loss decreases the longer you stay invested, which is why 401(k) plans are designed for long-term retirement savings.
What’s the difference between a 401(k) and an IRA?
The main differences between 401(k) plans and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) include:
- Contribution limits: 401(k)s have much higher contribution limits (,500 vs. ,000 for IRAs in 2025)
- Employer involvement: 401(k)s are employer-sponsored with potential matching contributions; IRAs are individual accounts
- Investment options: 401(k)s offer limited options selected by the plan; IRAs provide access to a wider range of investments
- Required Minimum Distributions: Traditional 401(k)s and IRAs both require RMDs; Roth 401(k)s require RMDs while Roth IRAs do not
- Loan provisions: Many 401(k) plans allow loans; IRAs do not
Can I have multiple 401(k) accounts?
Yes, you can have multiple 401(k) accounts, especially if you’ve left them with previous employers. However, your annual contribution limit applies across all your 401(k) accounts combined, not to each account separately. Many financial advisors recommend consolidating old 401(k)s either into your current employer’s plan or into an IRA to simplify management and potentially reduce fees.