Use our Interest Rate Calculator to determine interest rates for loans or savings. Plan finances, compare rates, and make informed financial decisions easily.
Interest rates impact nearly every financial decision we make. Whether you're taking out a loan, saving for retirement, or investing in the market, understanding how interest rates work is crucial for making informed financial choices. Our Interest Rate Calculator helps you determine real interest rates on loans with fixed terms and monthly payments, giving you the clarity you need to make sound financial decisions.
How Our Interest Rate Calculator Works
Our Interest Rate Calculator is designed to help you determine the actual interest rate on loans, especially in situations where only the monthly payment information and total price are provided without the specific rate. This tool is particularly useful when evaluating car loans, mortgages, or personal loans where the true interest rate may not be immediately clear.
Our Interest Rate Calculator provides a simple interface for accurate interest rate determination
Ready to Calculate Your Interest Rate?
Use our comprehensive calculator to determine the exact interest rate on your loan or investment.
What is Interest Rate?
Interest rate is the amount charged by lenders to borrowers for the use of money, expressed as a percentage of the principal (original amount borrowed). It can also be described as the cost to borrow money. For instance, an 8% interest rate for borrowing $100 for a year will obligate a person to pay $108 at year-end.
As demonstrated in this simple example, the interest rate directly affects the total interest paid on any loan. Generally, borrowers want the lowest possible interest rates because it costs less to borrow, while lenders seek high interest rates for larger profits.
Interest rates are usually expressed annually, but they can also be expressed as monthly, daily, or any other period. They're involved in almost all formal lending and borrowing transactions, including:
- Mortgage rates for home purchases
- Credit card outstanding debt charges
- Business loans for capital projects
- Growth of retirement funds
- Amortization of long-term assets
- Early payment discounts offered by suppliers
Need to Calculate a Specific Interest Rate?
Our calculator handles various scenarios from mortgages to personal loans.
Simple vs. Compound Interest
There are two primary methods for calculating interest, each with different implications for borrowers and lenders:
Simple Interest
Simple interest is calculated as a percentage of the principal only. The formula is:
Interest = Principal × Interest Rate × Term
With simple interest, the interest amount remains the same each period because it's always calculated on the original principal.

Compound Interest
Compound interest is calculated as a percentage of the principal along with any accrued interest. This means interest earns interest over time.
The more frequently interest compounds within a given time period, the more interest will accrue.

Most formal interest payment calculations today use compound interest rather than simple interest. The power of compound interest becomes more apparent over longer time periods, which is why it's often referred to as "the eighth wonder of the world" in investment contexts.
Compare Simple vs. Compound Interest
See the dramatic difference compound interest makes over time.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Fixed Interest Rates
- Set as a certain percentage for the life of the loan
- Will not change regardless of market conditions
- Provides predictable payment amounts
- Easier to budget for over the long term
- Protects borrowers when market rates increase
Variable Interest Rates
- Can fluctuate over time based on market conditions
- Often start lower than fixed rates
- May increase unexpectedly, raising payment amounts
- Based on factors like inflation or market indices
- Can benefit borrowers when market rates decrease
Our Interest Rate Calculator displays results as a fixed interest rate. For variable rate calculations, you may need to recalculate as rates change over time.
Comparison of fixed vs. variable interest rates over a 10-year period
Understanding APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
The interest rate for many types of loans is often advertised as an annual percentage rate, or APR. APRs differ from typical interest rates in that certain fees can be packaged into them.
For instance, administrative fees that are usually due when buying new cars are typically rolled into the financing of the loan instead of paid upfront. APR provides a more accurate representation than the interest rate alone when shopping and comparing similar competing offers.
| Term | Definition | Primary Use |
| Interest Rate | The percentage charged on the principal amount only | Basic loan cost calculation |
| APR (Annual Percentage Rate) | Interest rate plus fees, expressed as a yearly rate | Comparing loan offers |
| APY (Annual Percentage Yield) | Interest rate that accounts for compounding | Savings accounts, CDs |
On the other hand, annual percentage yield (APY) is the interest rate that is earned at a financial institution, usually from a savings account or Certificate of Deposit (CD). APY accounts for compound interest, making it particularly relevant for savings and investments.
Economic Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Many factors influence the interest rates people receive on mortgages, auto loans, and other financial products. While individuals can't control these factors, understanding them can help you make more informed financial decisions.
Uncontrollable Economic Factors
Monetary Policy
Central banks like the Federal Reserve set monetary policy to control inflation. They can adjust interest rates up to eight times per year during committee meetings.
Economic Activity
When interest rates decrease, more businesses and individuals borrow money, creating jobs and boosting consumer confidence. When rates increase, fewer people borrow, slowing economic growth.
Unemployment Rate
High unemployment typically leads to lower interest rates to stimulate spending. Low unemployment can lead to higher rates to prevent inflation from rising too quickly.
Supply and Demand
When demand for credit is high, lenders may raise interest rates. When demand is low, they may lower rates to attract more borrowers.

How economic factors influence interest rates in the market
Calculate How Rate Changes Affect Your Payments
See how different interest rates impact your monthly payments and total cost.
Controllable Factors That Determine Your Interest Rate
While many factors affecting interest rates are beyond your control, there are several ways individuals can influence the rates they receive.

How your credit score affects the interest rates you receive
Individual Credit Standing
Your credit score is a number between 300 and 850 that represents your creditworthiness; the higher, the better. Good credit scores are built over time through timely payments, low credit utilization, and many other factors.
The higher your credit score, the more favorable interest rate you may receive. Scores above 750 are considered excellent and will receive the best interest rates. Lenders are more hesitant to lend to borrowers with low credit scores or a history of missed payments.
How to Receive Better Interest Rates
- Consider secured loans - Secured loans (backed by collateral) typically have lower interest rates than unsecured loans.
- Optimize loan specifics - Shorter loan terms and larger down payments can help you secure lower interest rates.
- Limit credit applications - Too many credit inquiries can lower your credit score and result in higher interest rates.
- Time your borrowing - When possible, borrow during economic slowdowns when demand for loans is lower and rates may be more favorable.
- Shop around - Different lenders offer different rates. Compare options and negotiate using competing offers.
See How Different Factors Affect Your Rate
Use our calculator to compare scenarios with different credit scores and loan terms.
Understanding Real Interest Rate
When discussing interest rates, it's important to distinguish between nominal and real interest rates. The relationship between real interest rate, inflation, and the nominal rate is shown by the following equation:
Real Interest Rate + Inflation = Nominal Interest Rate
In this equation, the nominal rate is generally the figure being discussed when the "interest rate" is mentioned. The nominal rate is the sum of the general level of inflation and the real rate of interest being applied.
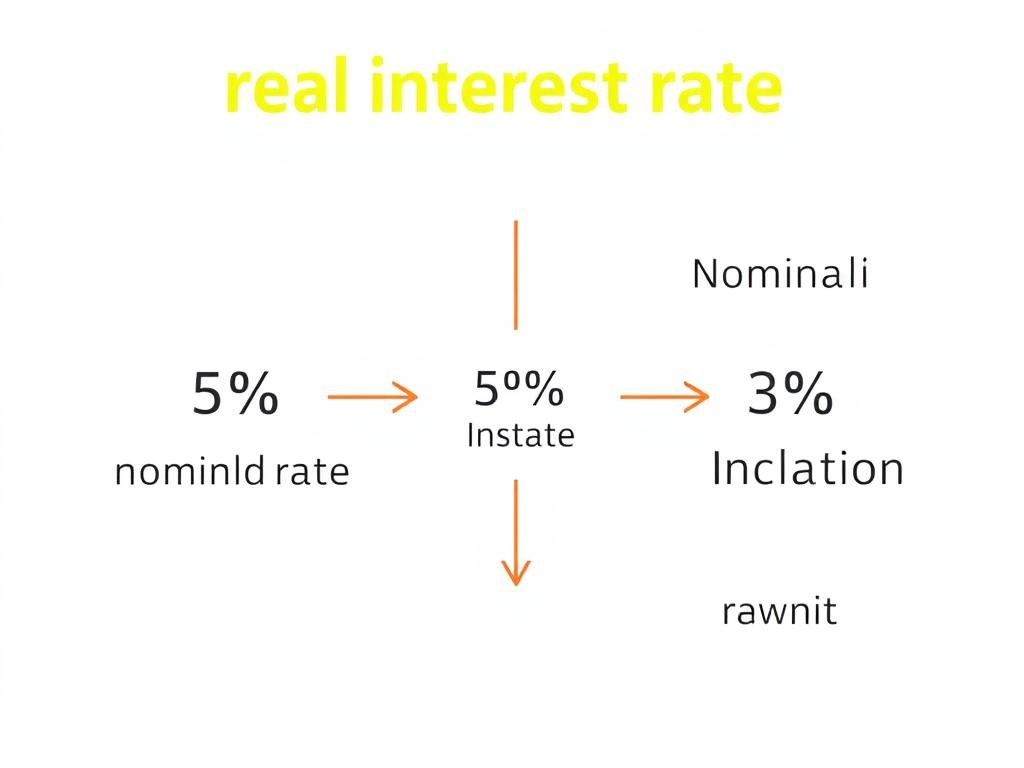
How real interest rate and inflation combine to form the nominal interest rate
For example, if the nominal interest rate on a loan is 6% and inflation is running at 2%, then the real interest rate is 4%. This means that while you're paying 6% in interest, the real cost of borrowing (after accounting for inflation) is only 4%.
Understanding the real interest rate is crucial for evaluating the true cost of borrowing or the actual return on investments. In periods of high inflation, a seemingly reasonable nominal interest rate might actually represent a negative real interest rate.
Practical Applications of the Interest Rate Calculator
For Borrowers
- Determine the true interest rate on a car loan when only the monthly payment is provided
- Calculate the effective interest rate on a mortgage to compare offers
- Understand the real cost of financing for major purchases
- Evaluate refinancing options by comparing current and offered rates

For Savers
- Calculate the effective interest rate on savings accounts
- Compare returns between different investment vehicles
- Determine how interest rates affect retirement planning
- Understand how inflation impacts the real return on savings
For Businesses
- Evaluate the cost of capital for business expansion
- Calculate the effective interest rate on business loans
- Determine the impact of interest rates on cash flow
- Compare financing options for equipment purchases

Ready to Apply This to Your Situation?
Our calculator helps you make informed financial decisions for any scenario.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Our Interest Rate Calculator
Follow these steps to accurately calculate interest rates using our calculator
Example Calculation
Let's say you're considering a car loan with the following details:
- Loan amount: $25,000
- Loan term: 60 months (5 years)
- Monthly payment: $483
Using our Interest Rate Calculator, you would enter these values and click "Calculate." The calculator would determine that the interest rate on this loan is approximately 5.9%.
With this information, you can now compare this offer with others or determine if the rate is reasonable based on your credit score and current market conditions.
Try It With Your Own Numbers
See what interest rate applies to your specific financial situation.
Making Informed Financial Decisions with Interest Rate Knowledge
Understanding interest rates is fundamental to making sound financial decisions. Whether you're comparing loan offers, planning for retirement, or evaluating investment opportunities, knowing how to calculate and interpret interest rates gives you the power to maximize your financial well-being.
Our Interest Rate Calculator provides a simple yet powerful tool to help you navigate the complex world of interest rates. By using this calculator, you can uncover the true cost of borrowing, compare different financial products accurately, and make decisions that align with your long-term financial goals.
Remember that interest rates are influenced by both macroeconomic factors beyond your control and personal factors you can improve. By maintaining good credit, shopping around for the best rates, and understanding how different loan terms affect your costs, you can secure more favorable interest rates and save significantly over time.
Start Calculating Your Interest Rates Today
Take control of your financial future with our comprehensive suite of calculators.
