Use our Lease Calculator to estimate monthly lease payments, total cost, and interest. Plan your vehicle or equipment lease and manage your budget effectively.
Understanding the true cost of a lease can be challenging with all the variables involved. Our lease calculator helps you determine accurate monthly payments for vehicles, equipment, or property leases. Whether you’re considering leasing a new car, commercial equipment, or real estate, this calculator breaks down all components to give you a clear financial picture before signing any agreement.
Lease Payment Calculator
Use this calculator to determine your estimated monthly lease payment based on the asset value, residual value, interest rate, and term length.
What is a Lease?
A lease is a contractual agreement between a lessor (the owner of an asset) and a lessee (the user of the asset) that grants the right to use the asset for a specified period in exchange for regular payments. Unlike purchasing, leasing doesn’t transfer ownership but provides temporary usage rights.

Leases are common for various assets including:
- Vehicles (cars, trucks, vans)
- Real estate (commercial and residential)
- Equipment (industrial, medical, office)
- Technology (computers, servers, software)
- Aircraft and watercraft
- Construction equipment
- Furniture and fixtures
- Agricultural machinery
The key difference between renting and leasing is the contract duration and terms. Renting typically involves shorter periods with more flexibility, while leasing involves longer commitments with more structured terms. Both arrangements avoid the need for full ownership but have different financial implications.
Understanding Lease Components
To accurately calculate lease payments, you need to understand the key components that influence the final amount. Each element plays a crucial role in determining your monthly obligation.
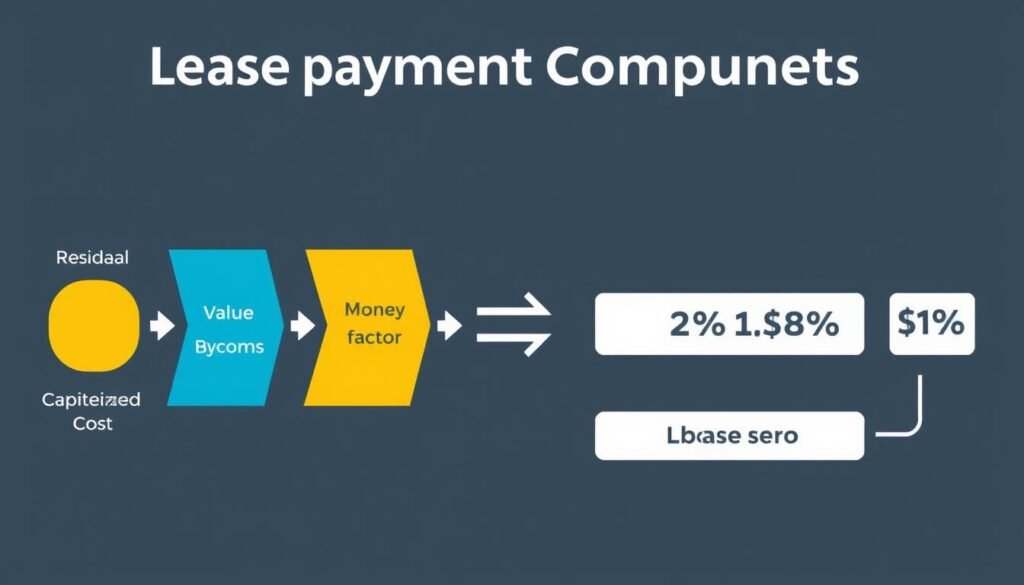
Capitalized Cost (Cap Cost)
The capitalized cost represents the amount being financed through the lease. For vehicles, this is typically the negotiated purchase price plus any additional fees or taxes that are rolled into the lease. Reducing the capitalized cost through negotiation or down payment directly lowers your monthly payments.
Residual Value
Residual value is the estimated worth of the asset at the end of the lease term. This value is predetermined by the leasing company based on projected depreciation. Higher residual values result in lower monthly payments since you’re only paying for the depreciation during your lease period plus interest.
Money Factor
The money factor is essentially the interest rate expressed in a different format. To convert a money factor to an annual percentage rate (APR), multiply it by 2,400. For example, a money factor of 0.00125 equals an APR of 3% (0.00125 × 2,400 = 3%). Lower money factors result in lower monthly payments.
Lease Term
The lease term is the duration of your lease agreement, typically expressed in months. Common lease terms range from 24 to 60 months, with 36 months being the most popular for vehicle leases. Longer terms generally result in lower monthly payments but may have other financial implications.
Taxes and Fees
Various taxes and fees may apply to your lease, including sales tax, acquisition fees, disposition fees, and registration fees. Some of these are paid upfront, while others are incorporated into the monthly payment. Tax treatment varies by location, with some jurisdictions taxing the entire lease amount and others only the monthly payments.
Lease Payment Calculation Formula
Understanding the mathematical formula behind lease calculations helps you verify the accuracy of quoted payments. The basic formula for calculating a monthly lease payment consists of two main components: the depreciation fee and the finance fee.
Monthly Lease Payment = Depreciation Fee + Finance Fee + Sales Tax
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Depreciation Fee = (Capitalized Cost – Residual Value) ÷ Lease Term in Months
Finance Fee = (Capitalized Cost + Residual Value) × Money Factor
Sales Tax = (Depreciation Fee + Finance Fee) × Tax Rate
Total Monthly Payment = Depreciation Fee + Finance Fee + Sales Tax

Practical Example
Let’s calculate a lease payment for a vehicle with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
| Vehicle Price (Negotiated) | $35,000 |
| Down Payment | $3,000 |
| Residual Value (55% of MSRP) | $19,250 |
| Money Factor | 0.00125 (3% APR) |
| Lease Term | 36 months |
| Sales Tax Rate | 7% |
Calculation steps:
- Capitalized Cost = $35,000 – $3,000 = $32,000
- Depreciation Fee = ($32,000 – $19,250) ÷ 36 = $354.17 per month
- Finance Fee = ($32,000 + $19,250) × 0.00125 = $64.06 per month
- Pre-Tax Payment = $354.17 + $64.06 = $418.23
- Sales Tax = $418.23 × 0.07 = $29.28
- Total Monthly Payment = $418.23 + $29.28 = $447.51
Auto Lease Calculators
Vehicle leases have specific considerations that make them different from other types of leases. Auto lease calculators are specialized tools designed to account for these unique factors.

Special Considerations for Auto Leases
Mileage Limits
Most auto leases include mileage restrictions, typically between 10,000 to 15,000 miles annually. Exceeding these limits results in excess mileage charges, usually between $0.15 to $0.30 per mile. Our calculator helps you factor in potential mileage charges based on your driving habits.
Wear and Tear Provisions
Lease agreements distinguish between normal and excessive wear and tear. Understanding these provisions helps you anticipate potential end-of-lease charges. Some lessees opt for wear and tear insurance to mitigate these risks.
Gap Insurance
Gap insurance covers the difference between what you owe on your lease and what the vehicle is worth if it’s totaled or stolen. This protection is often recommended for leased vehicles and may affect your overall leasing costs.
Disposition Fees
Many leases include disposition fees, typically $300-$500, charged when you return the vehicle and don’t purchase it. This fee covers the lessor’s costs of preparing the returned vehicle for resale.
Ready to Calculate Your Auto Lease?
Use our specialized auto lease calculator to get an accurate estimate of your monthly payments, including mileage considerations and other vehicle-specific factors.
Equipment Lease Calculators
Equipment leasing is common for businesses that need access to machinery, technology, or other assets without the large capital outlay of purchasing. Equipment lease calculators help businesses determine the financial implications of these arrangements.

Types of Equipment Leases
Operating Leases
Operating leases are typically shorter-term arrangements where the lessor maintains ownership of the equipment. These leases are often used for equipment that quickly becomes obsolete or requires frequent upgrades, such as computers or medical technology.
Capital/Finance Leases
Capital leases function more like financing arrangements for purchasing equipment. The lessee typically assumes most rights and responsibilities of ownership, and the lease often includes a bargain purchase option at the end of the term.
Tax Implications
Equipment leases have important tax considerations that differ from other types of leases. Operating leases generally allow the lessee to deduct lease payments as business expenses, while capital leases may enable depreciation deductions. Our calculator helps businesses understand these implications for more informed decision-making.
Calculate Your Equipment Lease Payments
Determine the most cost-effective leasing structure for your business equipment needs with our specialized calculator.
Real Estate Lease Calculators
Real estate leases, whether commercial or residential, involve unique considerations that affect payment calculations. Our real estate lease calculator accounts for these specific factors to provide accurate estimates.

Commercial Lease Types
Gross Lease
In a gross lease, the tenant pays a flat rental amount while the landlord covers most expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance. This simplifies budgeting for tenants but typically comes at a premium.
Net Lease
Net leases require tenants to pay a base rent plus some portion of property expenses. Triple net (NNN) leases, the most common type, require tenants to pay all property expenses in addition to rent.
Modified Lease
Modified leases represent a middle ground between gross and net leases, with specific expense responsibilities negotiated between landlord and tenant. These arrangements require careful calculation to understand the true cost.
Residential Lease Considerations
Residential leases typically involve security deposits, potential rent increases, and utility arrangements that affect the total cost of leasing. Our calculator helps tenants understand the complete financial picture beyond the base monthly rent.
Calculate Your Real Estate Lease
Whether you’re considering a commercial or residential property lease, our calculator helps you understand the true cost of your agreement.
Lease vs. Buy: Making the Right Decision
One of the most common financial dilemmas is whether to lease or buy an asset. Our calculator helps you compare these options to make an informed decision based on your specific circumstances.
Benefits of Leasing
- Lower monthly payments
- Minimal upfront costs
- Ability to upgrade to newer models regularly
- Reduced maintenance concerns (especially with warranties)
- Potential tax advantages for businesses
- No long-term commitment to depreciating assets
Benefits of Buying
- Build equity and ownership
- No mileage restrictions or wear penalties
- Freedom to modify or customize
- Lower long-term costs (after loan payoff)
- No recurring lease cycles
- Potential resale value
Financial Comparison
The financial implications of leasing versus buying depend on several factors, including how long you plan to keep the asset, its depreciation rate, available interest rates, and your tax situation. Our calculator incorporates these variables to provide a comprehensive comparison.
| Factor | Leasing Impact | Buying Impact |
| Upfront Cost | Lower (typically first month’s payment plus security deposit) | Higher (down payment typically 10-20%) |
| Monthly Payment | Lower (paying only for depreciation during lease term) | Higher (paying for entire asset plus interest) |
| Long-term Cost | Higher (continuous payments with no equity) | Lower (payments eventually end, retain asset value) |
| Flexibility | Higher (easier to upgrade or change) | Lower (must sell or trade to change) |
| Tax Benefits | Potentially higher for businesses (entire payment may be deductible) | Depreciation and interest deductions for businesses |
Compare Leasing vs. Buying
Use our comprehensive calculator to compare the financial implications of leasing versus buying for your specific situation.
Tips for Negotiating Better Lease Terms
Understanding how lease calculations work gives you an advantage when negotiating terms. Here are strategies to secure more favorable lease arrangements.

Negotiate the Capitalized Cost
The capitalized cost has the most significant impact on your monthly payment. Research fair market values before negotiations and treat a lease negotiation like a purchase negotiation. Focus on reducing the vehicle or asset price first, before discussing lease terms.
Understand the Money Factor
The money factor is essentially your interest rate. Ask for the money factor and convert it to an APR by multiplying by 2,400. Compare this rate with current market rates to ensure you’re getting a competitive offer. Your credit score significantly impacts this rate.
Consider Residual Value
A higher residual value leads to lower monthly payments. Research which assets hold their value better. However, be cautious if you’re considering purchasing at lease-end, as a high residual value means a higher purchase price.
Minimize Down Payments
Unlike purchasing, down payments on leases don’t build equity. They simply reduce the capitalized cost. Consider whether those funds might be better invested elsewhere, especially if the money factor (interest rate) is low.
Watch for Hidden Fees
Acquisition fees, disposition fees, and excessive wear charges can significantly impact the total cost of leasing. Ask for a complete breakdown of all fees and negotiate to reduce or eliminate them where possible.
Match Terms to Usage
Align your lease term and mileage allowance with your actual needs. Overestimating mileage increases your payment unnecessarily, while underestimating can result in costly excess mileage charges at lease-end.
Pro Tip: Use our lease calculator during negotiations to quickly evaluate how different terms affect your monthly payment. This real-time analysis gives you leverage to secure the most favorable arrangement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease Calculations

What happens if I want to end my lease early?
Early lease termination typically involves significant costs. Most leases require payment of all remaining lease payments plus early termination fees. Some options to mitigate these costs include:
- Lease transfer/assumption (if permitted by the lessor)
- Lease buyout and vehicle resale (though you may face negative equity)
- Trading in the leased vehicle for a new lease (the dealer may roll remaining payments into the new lease)
Use our calculator to determine the financial impact of early termination compared to completing your lease term.
How does my credit score affect my lease payment?
Your credit score primarily affects the money factor (interest rate) of your lease. Higher credit scores qualify for lower money factors, resulting in lower monthly payments. Some lessors also require larger security deposits or down payments from lessees with lower credit scores to offset perceived risk.
Can I negotiate the residual value of a lease?
Residual values are typically set by leasing companies or banks, not dealers, and are generally non-negotiable. They’re based on projected future value using industry data. However, you can shop different manufacturers who may offer more favorable residual values on comparable assets, effectively lowering your monthly payment.
How are taxes calculated on leases?
Tax treatment varies by jurisdiction. In some areas, sales tax applies to the entire value of the leased asset upfront. More commonly, sales tax is applied only to the monthly payments. Some states also have specific taxes or fees for leased vehicles. Our calculator can be adjusted to account for your local tax situation.
Should I make a down payment on a lease?
Unlike purchasing, down payments on leases (often called capitalized cost reductions) don’t build equity. They simply reduce your monthly payment by lowering the capitalized cost. Financial experts often advise minimizing down payments on leases, as that money could potentially earn better returns elsewhere. Additionally, if the leased asset is totaled or stolen early in the lease term, you typically don’t recover your down payment.
Making Informed Leasing Decisions
Understanding lease calculations empowers you to make financially sound decisions when considering lease agreements. By using our comprehensive lease calculator, you can accurately determine monthly payments, compare different lease options, and negotiate more favorable terms.
Whether you’re leasing a vehicle, equipment, or property, the fundamental principles of lease calculations remain consistent. Focus on the key components that affect your payment: capitalized cost, residual value, money factor, and lease term. By optimizing these variables, you can secure a lease arrangement that aligns with your financial goals and usage needs.
Start Calculating Your Lease Payment
Use our lease calculator to get an accurate estimate of your monthly obligations and make an informed decision.